NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around Us Pure include can be downloaded from this article in PDF. These solutions are prepared by the subject experts. All the answers have been explained in the easiest manner to help students clear the concepts and perform well in their Science exam.
Also Read: CBSE Class 9 Science Syllabus 2022-23 (Download in PDF)
Multiple Choice Questions
1.Which of the following statements are true for pure substances?
(i) Pure substances contain only one kind of particles
(ii) Pure substances may be compounds or mixtures
(iii) Pure substances have the same composition throughout
(iv) Pure substances can be exemplified by all elements other than nickel
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer: (b) (i) and (iii)
Explanation: A pure substance is one which is made up of only one kind of atoms or molecules. They have the same composition throughout.
2.Rusting of an article made up of iron is called
(a) corrosion and it is a physical as well as chemical change
(b) dissolution and it is a physical change
(c) corrosion and it is a chemical change
(d) dissolution and it is a chemical change
Answer: (c) corrosion and it is a chemical change.
Explanation:
Rusting of iron is corrosion and it’s a chemical change because the compound so formed Fe2O3.nH2O (hydrated iron oxide) has totally different composition and properties from the reactants (iron, moisture)
3.A mixture of sulphur and carbon disulphide is
(a) heterogeneous and shows Tyndall effect
(b) homogeneous and shows Tyndall effect
(c) heterogeneous and does not show Tyndall effect
(d) homogeneous and does not show Tyndall effect
Answer: (a) heterogeneous and shows Tyndall effect.
Explanation:
A mixture of sulphur and carbon disulphide is heterogeneous and shows Tyndall effect because in a colloidal solution the particles are big enough to scatter light. The scattering of light by colloidal particles is known as Tyndall effect. Colloids are actually heterogeneous in nature.
4.Tincture of iodine has antiseptic properties. This solution is made by dissolving
(a) iodine in potassium iodide
(b) iodine in vaseline
(c) iodine in water
(d) iodine in alcohol
Answer: (d) iodine in alcohol
Explanation:
Tincture is prepared by using 2-7% elemental iodine and either of potassium iodide or sodium dissolved in alcohol.
5.Which of the following are homogeneous in nature?
(i) ice
(ii) wood
(iii) soil
(iv) air
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (c) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Air and ice are homogeneous mixture because their constituting elements are not visible and cannot be distinguished from one another.
6.Which of the following are physical changes?
(i) Melting of iron metal
(ii) Rusting of iron
(iii) Bending of an iron rod
(iv) Drawing a wire of iron metal
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Explanation: In all the three processes only the shape or form of iron changes but its chemical composition remains the same.
7.Which of the following are chemical changes?
(i) Decaying of wood
(ii) Burning of wood
(iii) Sawing of wood
(iv) Hammering of a nail into a piece of wood
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer: (a) (i) and (ii)
Explanation
In decaying and burning of wood, there will be a change of chemical composition of wood. Moreover, wood cannot be restored to its original form.
8.Two substances, A and B were made to react to form a third substance, A2B according to the following reaction 2A + B → A2B which of the following statements concerning this reaction are incorrect?
(i) The product A2B shows the properties of substances A and B
(ii) The product will always have a fixed composition
(iii) The product so formed cannot be classified as a compound
(iv) The product so formed is an element
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii),
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (c) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Explanation:
A2B is a compound made up of two elements A and B in a fixed ratio. The properties of a compound are entirely different from those of its constituent elements. The composition of a compound is fixed.
9.Two chemical species X and Y combine together to form a product P which contains both X and Y X + Y → P. X and Y cannot be broken down into simpler substances by simple chemical reactions. Which of the following concerning the species X, Y and P are correct?
(i) P is a compound
(ii) X and Y are compounds
(iii) X and Y are elements
(iv) P has a fixed composition
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii),
(b) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer: (d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Explanation: Here X and Y cannot be further broken down into simpler substances, hence they are elements while P which made up of X and Y is a compound as it can be broken down to its elements. Compounds have a fixed composition.
Short Answer Questions
10.Suggest separation technique(s) one would need to employ to separate the following mixtures.
(a) Mercury and water
(b) Potassium chloride and ammonium chloride
(c) Common salt, water and sand
(d) Kerosene oil, water and salt
Answer:
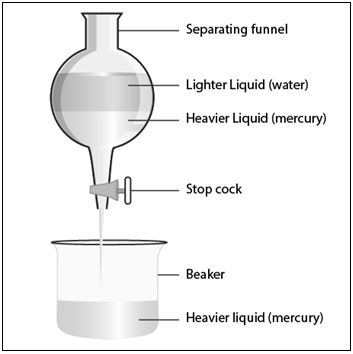
(a) Decantation: This method is used to separate the mixture of Mercury and water as they have different densities. Here Mercury is heavier than water hence it forms a lower layer which can be easily separated in separating funnel.
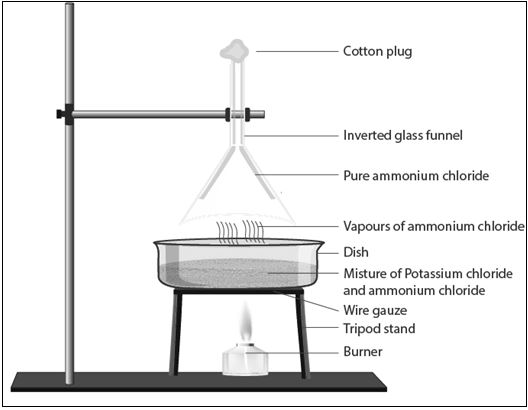
(b) Potassium chloride and ammonium chloride are separated by sublimation method because ammonium chloride has the property of directly changing into vapours (which is called sublimation). Thus, potassium chloride is collected a residue.
(c) Common salt, water and sand are separated by filtration followed by the evaporation processes. The mixture is filtered to separate the sand from salt solution. After that the salt solution is heated to evaporate the water leaving behind salt.
(d) Kerosene oil is separated from salt solution in water by the decantation process using a separating funnel in which kerosene being heavier forms a separate layer. Then salt is separated from water by the process of evaporation.
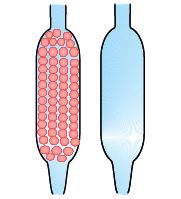
11.Which of the tubes in Fig. 2.1
(a) and (b) will be more effective as a condenser in the distillation apparatus?
Answer: Tube (a) will be more effective as a condenser in the distillation apparatus. This is because beads in tube A provide an increased surface area for cooling of the vapours that come in contact with them. Hence, it is a good condenser.
12.Salt can be recovered from its solution by evaporation. Suggest some other technique for the same?
Answer: Crystallization can be used to recover salt from its solution by evaporation.
13.The ‘sea-water’ can be classified as a homogeneous as well as heterogeneous mixture. Comment.
Answer:
Sea-water is called homogeneous as it contains dissolved salts in it. It can be considered as heterogeneous as it contains various insoluble components like sand, microbes, shells made of calcium carbonate, etc.
14.While diluting a solution of salt in water, a student by mistake added acetone (boiling point 56°C). What technique can be employed to get back the acetone? Justify your choice.
Answer:
Fractional Distillation can be used to separate acetone from the mixture of salt and water.
Both acetone and water have different boiling points (56°C and 100°C respectively). So, when the solution is heated acetone evaporates first and the water is collected in the distillation flask. The vapours of acetone are then condensed to obtain acetone.
15.What would you observe when
(a) a saturated solution of potassium chloride prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool to room temperature.
(b) an aqueous sugar solution is heated to dryness.
(c) a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly.
Answer:
(a) When a saturated solution of potassium chloride prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool at room
temperature, potassium chloride will separate in the form of crystals.
(b) When aqueous sugar solution is heated first water gets evaporated leaving behind sugar but on dry heating sugar gets charred.
(c) When a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly Iron combines with sulphur and forms iron sulphide (FES).
16.Explain why particles of a colloidal solution do not settle down when left undisturbed, while in the case of a suspension they do.
Answer:
The size of colloidal particles is relatively smaller. They continue to move in a zig-zag pattern, avoiding the force of gravity and do not settle down. On the other hand, the suspension particles are larger and heavier than colloidal particles due to which they settle down under the influence of gravity.
17.Smoke and fog both are aerosols. In what way are they different?
Answer:
Both smoke and fog have gas as the dispersion medium. But they differ in respect of the dispersed phase. Dispersed phase in fog is liquid (water particles) whereas in smoke it is solid (carbon particles).
18.Classify the following as physical or chemical properties
(a) The composition of a sample of steel is 98% iron, 1.5% carbon and 0.5% other elements.
(b) Zinc dissolves in hydrochloric acid with the evolution of hydrogen gas.
(c) Metallic sodium is soft enough to be cut with a knife.
(d) Most metal oxides form alkalis on interacting with water.
Answer:
(a) Composition of a sample of steel is 98% iron, 1.5% carbon and 0.5% other elements. It is a physical property because no new compound is formed as the steel is an alloy and alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals or of metallic elements with non-metallic elements.
(b) It is a chemical property because zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid to give out zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
(c) The cutting of metallic sodium with knife is a physical property as it does not form any new compound.
(d) It is a chemical property as the new compound is formed by the reaction of metal oxide and water.
19.The teacher instructed three students ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ respectively to prepare a 50% (mass by volume) solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). ‘A’ dissolved 50g of NaOH in 100 mL of water, ‘B’ dissolved 50g of NaOH in 100g of water while ‘C’ dissolved 50g of NaOH in water to make 100 mL of solution. Which one of them has made the desired solution and why?
Answer:
Student C has made the desired solution because he added 50 g of solute for every 100 mL of solution. On the other hand, both A and B prepare 150 ml solution,
Mass by Volume % = (Mass of solute/ Volume of Solution) × 100
= (50/100) × 100 =50% mass by volume
20.Name the process associated with the following
(a) Dry ice is kept at room temperature and at one atmospheric pressure.
(b) A drop of ink placed on the surface of water contained in a glass spreads throughout the water.
(c) A potassium permanganate crystal is in a beaker and water is poured into the beaker with stirring.
(d) An acetone bottle is left open and the bottle becomes empty.
(e) Milk is churned to separate cream from it.
(f) Settling of sand when a mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed for some time.
(g) Fine beam of light entering through a small hole in a dark room, illuminates the particles in its paths
Answer:
(a) Sublimation
(b) Diffusion
(c) Dissolution/ diffusion
(d) Evaporation
(e) Centrifugation
(f) Sedimentation
(g) Tyndall effect
21.You are given two samples of water labelled as ‘A’ and ‘B’. Sample ‘A’ boils at 100°C and sample ‘B’ boils at 102°C. Which sample of water will not freeze at 0°C? Comment.
Answer:
The boiling point of water is 100°C while the boiling point of sample B is 102°C. This means the sample B contains impurities. Therefore, sample B will not freeze at 0°C.
22.What are the favourable qualities given to gold when it is alloyed with copper or silver for the purpose of making ornaments?
Answer:
Pure gold is soft and brittle. In order to give strength to gold, it is alloyed with copper or silver. With this gold becomes harder and stronger which is suitable for making ornaments.
23.An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess?
Answer:
The element which is sonorous and highly ductile can be classified as metal. Other characteristics possessed by this element will include lustre, malleability, heat and electrical conductivity.
24.Give an example each for the mixture having the following characteristics. Suggest a suitable method to separate the components of these mixtures
(a) A volatile and a non-volatile component.
(b) Two volatile components with appreciable difference in boiling points.
(c) Two immiscible liquids.
(d) One of the components changes directly from solid to gaseous state.
(e) Two or more coloured constituents soluble in some solvent.
Answer:
(a) Example: Mixture of acetone and water.
Separation method: It can be separated by distillation.
(b) Example: Mixture of petrol and kerosene.
Separation method: It can be separated by distillation.
(c) Example: Mixture of oil and water.
Separation method: It can be separated by fractional distillation.
(d) Example: Mixture of naphthalene and ammonium chloride.
Separation method: Naphthalene can be separated from an aqueous solution by filtration and then ammonium chloride can be evaporated to obtain dry ammonium chloride.
(e) Example: Mixture of pigments from an extract of flower petals.
Separation method: It can be separated by chromatography.
25.Fill in the blanks
(a) A colloid is a ——— mixture and its components can be separated by the technique known as ———.
(b) Ice, water and water vapour look different and display different —— properties but they are ——— the same.
(c) A mixture of chloroform and water taken in a separating funnel is mixed and left undisturbed for some time. The upper layer in the separating funnel will be of——— and the lower layer will be that of ———.
(d) A mixture of two or more miscible liquids, for which the difference in the boiling points is less than 25 K can be separated by the process called———.
(e) When light is passed through water containing a few drops of milk, it shows a bluish tinge. This is due to the ——— of light by milk and the phenomenon is called ——— . This indicates that milk is a ——— solution.
Answer:
(a) heterogeneous, centrifugation
(b) physical, chemically
(c) water, chloroform
(d) distillation
(e) scattering, tyndall effect, colloidal
26.Sucrose (sugar) crystals obtained from sugarcane and beetroot are mixed together. Will it be a pure substance or a mixture? Give reasons for the same.
Answer:
sugar obtained by different sources like sugarcane and beetroot will have the same composition irrespective of its source. Therefore, it will be a pure substance.
27.Give some examples of Tyndall effect observed in your surroundings?
Answer:
(i)The beam of light passing on screen in a theatre.
(ii) When light passes through a dark room.
28.Can we separate alcohol dissolved in water by using a separating funnel? If yes, then describe the . If not, explain.
Answer:
We cannot separate alcohol dissolved in water by separating funnel as they both are miscible.
29.On heating calcium carbonate gets converted into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
(a) Is this a physical or a chemical change?
(b) Can you prepare one acidic and one basic solution by using the products formed in the above process? If so, write the chemical equation involved
Answers:
(a) It is a chemical change because the composition of product formed is different from the reacting elements.
CaCO3+H2O → CaO+CO2
(b) CaO on dissolving in water forms calcium hydroxide which is a basic solution.
CaO+H2O → Ca(OH)2 (basic solution)
When CO2 dissolves in water it forms carbonic acid which is acidic solution.
CO2 + H2O→H2CO3 (acidic solution)
30.Non-metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
(a) Name a lustrous non-metal.
(b) Name a non-metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature.
(c) The allotropic form of a non-metal is a good conductor of electricity. Name the allotrope.
(d) Name a non-metal which is known to form the largest number of compounds.
(e) Name a non-metal other than carbon which shows allotropy.
(f) Name a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Answer:
(a) Iodine is a lustrous non-metal.
(b) Bromine is non- mental which is liquid at room temperature
(c) Graphite is an allotropic form of Carbon (non-metal) which is a good conductor of electricity.
(d) Carbon is a non-metal which is known to form the largest number of compounds.
(e) Sulphur and Phosphorous are the non-metals which show allotropy.
(f) Oxygen is a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Answers to the remaining questions will be made available here shortly.
Also Read: NCERT Exemplar Problems for Class 9 Science (All Chapters)
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation