The United States Army was founded in 1775, making it the oldest military branch in the United States. It is one of the six branches of the U.S. Armed Forces, along with the Navy, Air Force, Marine Corps, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The US Army is responsible for land-based military operations. “This We’ll Defend” is the motto upheld by each of the US Army soldiers.
The Army's command structure is divided into three main categories: enlisted ranks, warrant officer ranks, and commissioned officer ranks. Enlisted ranks make up the majority of the Army, and they are responsible for carrying out the day-to-day operations of the military to ensure mission success. Warrant officers are technical experts, combat leaders, trainers, and advisors. Officer ranks manage personnel, assign orders, and carry out mission operations.
In this article, check the complete list of the US Army Ranks and Insignia in order.
US Army Ranks & Insignia, Complete List In Order
The U.S. Army ranks are broken down into three groups: Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-9), Warrant Officer Ranks (W-1 to W-5), and Commissioned Officer Ranks (O-1 to O-10). There are 13 enlisted ranks, 5 warrant officer ranks, and 11 officer ranks (the General of the Army is reserved for wartime only).
One should not confuse the rank with paygrade such as E-1, W-1, and O-1. Paygrades are administrative classifications used to determine a soldier's salary. The "E" in E-1 stands for "enlisted" while the "1" indicates the paygrade for that position. The other pay categories are "W" for warrant officers and "O" for commissioned officers. Some enlisted paygrades have two ranks, such as E-4 (specialist or corporal).
Enlisted Ranks
As per the Department of Defense, service members in paygrades E-1 through E-3 are usually either in some kind of training status or on their initial assignment. Junior enlisted are the most basic ranks in the Army. They are responsible for learning the basics of military life and performing basic tasks.
Private is the lowest Army rank and is short for private soldier. They have no uniform insignia. It is normally held only by new recruits. Specialist is considered one of the junior enlisted ranks in the US Army.
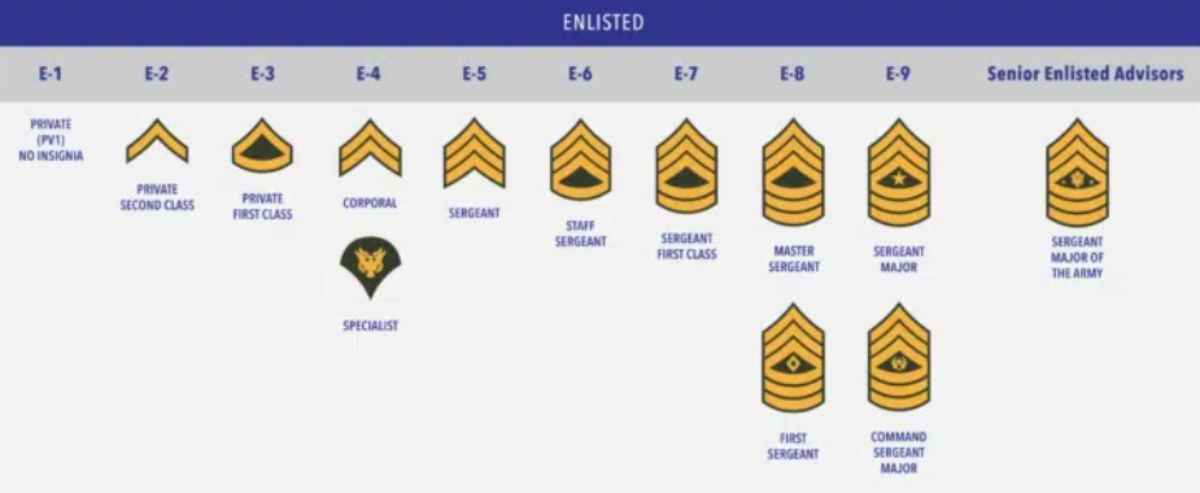
| Rank | Enlisted Personnel |
| E-1 | Private |
| E-2 | Private Second Class |
| E-3 | Private First Class |
| E-4 | Corporal |
| E-4 | Specialist |
| E-5 | Sergeant |
| E-6 | Staff Sergeant |
| E-7 | Sergeant First Class |
| E-8 | Master Sergeant |
| E-8 | First Sergeant |
| E-9 | Sergeant Major |
| E-9 | Command Sergeant Major |
| E-9S | Sergeant Major of the Army |
Warrant Officer Ranks
US Army Warrant officers are technical experts who specialize in a particular field, such as aviation, engineering, or intelligence. Warrant Officer 1 is the lowest warrant officer rank.

| Rank | Warrant Officer Personnel |
| W-1 | Warrant Officer 1 |
| W-2 | Chief Warrant Officer 2 |
| W-3 | Chief Warrant Officer 3 |
| W-4 | Chief Warrant Officer 4 |
| W-5 | Chief Warrant Officer 5 |
Commissioned Officer Ranks
Commissioned officers hold the highest ranks in the US Army. Second Lieutenant is the entry-level rank for most commissioned officers. General is the senior-level commissioned officer with over 30 years of experience and service. The General of the Army is only used in times of war.
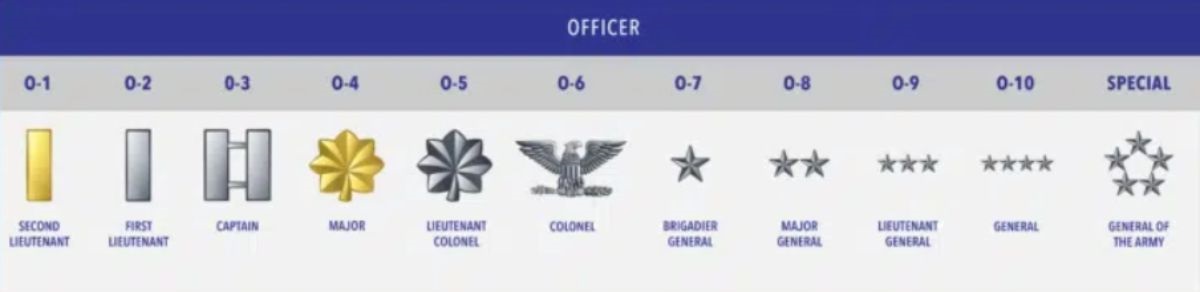
| Rank | Commissioned Officer Personnel |
| O-1 | Second Lieutenant |
| O-2 | First Lieutenant |
| O-3 | Captain |
| O-4 | Major |
| O-5 | Lieutenant Colonel |
| O-6 | Colonel |
| O-7 | Brigadier General |
| O-8 | Major General |
| O-9 | Lieutenant General |
| O-10 | General |
|
| General of the Army (reserved for wartime only) |
By now, you should be able to understand the US Army rank structure, and the difference between enlisted, warrant, and commissioned officer ranks in the US Army.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation