Who doesn’t know Elon Musk, the richest man in the world, with a staggering net worth of over $400 billion? He co-founded seven companies, including electric car maker Tesla, rocket producer SpaceX and artificial intelligence startup xAI. Starlink is the world's leading satellite constellation in low Earth orbit, offering high-speed, low-latency broadband internet globally.
Starlink is connecting more than 6M people with high-speed internet across 140 countries, territories and many other markets.
— Starlink (@Starlink) June 9, 2025
Thank you to all our customers around the world! 🛰️🌎❤️ → https://t.co/QnC5HG3geE pic.twitter.com/2OYEQr6S3o
It's built on advanced satellite technology and a wealth of experience in spacecraft operations, making it capable of supporting demanding applications like streaming and online gaming.
What is Starlink?
Starlink is a satellite internet service run by Starlink Services, a company fully owned by the American aerospace company SpaceX. It currently provides internet to about 130 countries and areas and plans to offer mobile internet everywhere. Starlink has been a big part of SpaceX's success.
SpaceX started sending Starlink satellites into space in 2019. As of May 2025, over 7,600 small satellites are orbiting Earth at a low altitude. These satellites talk to special equipment on the ground, and Starlink now makes up 65% of all active satellites in orbit.
SpaceX plans to launch nearly 12,000 satellites in total, with the potential to go up to 34,400. Starlink reached over 1 million subscribers by December 2022 and 4 million by September 2024.
How Does Starlink Work?
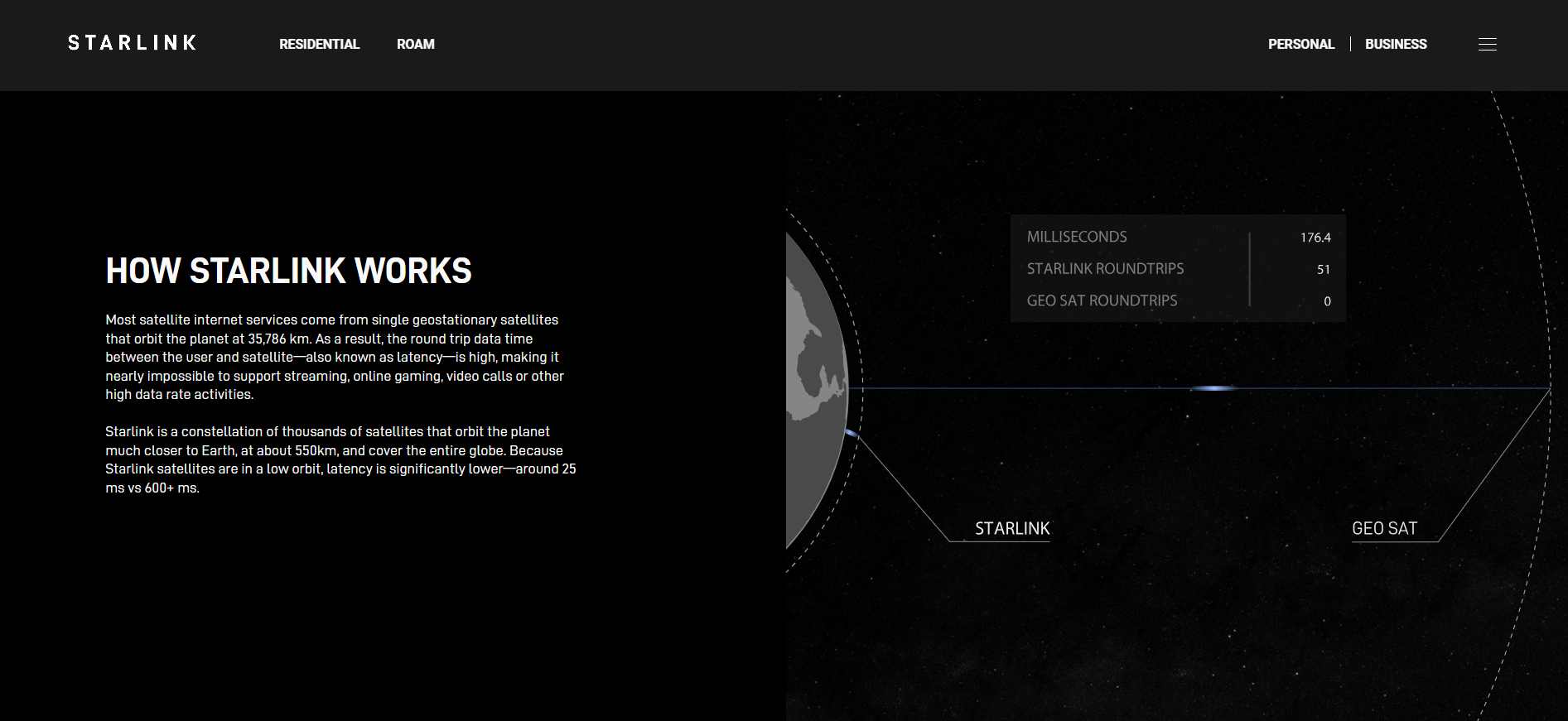
- Satellite Constellation: Starlink consists of thousands of small satellites orbiting the Earth at low altitudes (around 540 kilometres to 570 kilometres). This low Earth orbit (LEO) configuration helps reduce latency compared to traditional satellite internet systems that use geostationary satellites.
- Ground Stations: Starlink utilises a network of ground stations, known as gateway stations, that are strategically located around the globe. These stations connect the satellite network to the Internet backbone.
- User Terminals: Users access the Starlink service through a user terminal, often referred to as a satellite dish or antenna. This dish is equipped with phased-array technology, allowing it to electronically steer its beam to track satellites as they move across the sky.
- Data Transmission: When a user sends data (such as a web request), the signal travels from the user terminal to the nearest Starlink satellite. The satellite then relays the data to a ground station, which connects to the broader internet. The response follows the same path in reverse.
- Low Latency and High Speed: The combination of LEO satellites and advanced technology enables Starlink to offer lower latency (typically around 20-40 milliseconds) and high-speed internet (speeds ranging from 50 Mbps to over 150 Mbps), making it competitive with terrestrial internet services.
- Global Coverage: As more satellites are launched and become operational, Starlink aims to provide global coverage, including areas where traditional internet infrastructure is lacking or non-existent.
Starlink is a satellite internet service that works by transmitting data between a user's location and satellites orbiting the Earth. But do you know the real reason why they are making waves in the market?
Satellite Internet is best for those living in remote areas where big towers are not feasible to set up, providing high-speed internet access to underserved communities. You don't have to worry about connectivity issues due to weather conditions or physical obstacles, as the satellites are constantly moving to maintain a strong signal.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation