Biotechnology Principles and Processes CBSE Notes: To revise effectively and quickly, revision notes are the best option. These are the short notes that cover important topics of the chapter along with important diagrams. Students just need to give them a quick look to remember what they have learned.
With the revision made by CBSE to its syllabus, NCERT has also revised its textbooks. Thus, having notes on the revised content is important. In this article, you will find the revision notes for CBSE Class 12 Biology from Biotechnology Principles and Processes. After revision, this chapter is now numbered as Chapter 9 of the NCERT Class 12 Biology textbook. Read and download the revision notes below.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Biotechnology Principles and Processes Revision Notes
Important Terms
| 1 rDNA- Recombinant DNA 2 Gene cloning- DNA technology used to multiply the copies of a gene to increase the yield of its products. 3 Gene transfer- Transferring a DNA segment or gene from one organism to another. 4 Genetic Engineering- Manipulating the genetic material of cells or organisms to enable them to make new substances or perform new functions. 5 ori- The specific sequence of DNA which initiates replication. 6 Restriction enzymes- Enzymes that cut the DNA at specific sites. Also called as molecular scissors. 7 Plasmid- Autonomously replicating extrachromosomal circular DNA. 8 Cloning Vectors- Vectors that introduce foreign DNA into host cells. 9 Endonuclease- Restriction enzymes that recognise specific sequences within the DNA sequence. 10 Nucleases- Restriction enzymes that are specific to digest nucleic acids. 11 Exonucleases- Restriction enzyme that cleaves nucleotides sequentially from free ends of a linear Nucleic acid substrate. 12 Palindromic sequences- The sequence of base pairs that reads the same on both the strands when read in the same orientation (i.e. 5' to 3' in both the strands) 13 Gel Electrophoresis- A method of separating fragments of DNA molecule on an agarose gel. 14 Elution- The extraction of separated fragments of DNA from the electrophoresis gel. 15 Autoradiography- A technique that uses X-Ray film to visualise radioactively labelled molecules or fragments of molecules. 16 Transformation- A procedure in which bacterial cells take up DNA from the surrounding environment and get transformed. 17 Selectable markers- A gene or other identifiable portion of DNA whose inheritance can be followed and used in the process of selection of transformed cells from non-transformed ones. 19 Insertional Inactivation- The process by which a gene encoding a protein is inactivated by the insertion of a foreign DNA within the coding sequence of the protein 19 Ti Plasmid- Tumour inducing Plasmid in Agrobacterum sp. causing tumour in plant cells. 20 Tumour- Uncontrolled growth of cells in the body of plants or animals. 21 Microinjection- The process of introducing rDNA into animal cells using a micropipette 22 Biolistics/gene gun- A direct gene transfer method for delivering foreign genes into any tissues and cells or even seedlings. * The foreign DNA is coated or precipitated onto the surface of minute gold or tungsten particles * It is bombarded or shot onto the target tissue or cells using the gene gun. 23 Embryonic stem(ES) cells- An embryonic cell having totipotency that can replicate indefinitely, transform into other types of cells ,and serve as a continuous source of new cells. These cells are derived from inner cell mass of the blastocyst or the 4-9 cell stage of embryo. 24 Lysozyme- The enzyme that digests the cell wall of bacteria. 25 Cellulase- The enzyme that digests cellulose of plant cell walls. 26 Chitinase- The enzyme that can digest cell walls of fungi which contains chitin. 27 Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)- Polymerase Chain Reaction where DNA can be amplified in a short time to produce multiple copies of DNA (can be made in vitro). 29 Recombinant protein- Protein encoding gene expressed in a heterologous host 29 Bioreactors- Are vessels in which raw materials are Biologically converted into products using microbial,plant or animal cells 30 Downstream- Processing The process of formulation,separation and purification of rDNA products made in Bioreactors. 31 Spooling- The method of separating DNA precipitates in chilled ethanol ,after its isolation from the other cell contents. 32 Disarmed pathogens- Some bacteria or viruses,which are used to transfer recombinant DNA carrying the gene of interest to thehost cells. 33 Retrovirus- RNA virus containing reverse transcriptase and can be used to transfer the gene of interest into the host chromosome. 34 Ligases- Enzymes that can join fragments of DNA. 35 Vector- A molecule,capable of replication in a host organism,into which a gene is inserted to construct a recombinant DNA molecule. 36 Competent Host- Cell A cell which has been chemically treated to take up rDNA from its surroundings through pores in its cell wall. 37 Amplification- An increase in the number of copies of a specific DNA fragment; can be in vivo or in vitro. 39 Sticky ends- Single-stranded overhanging ends of DNA formed by the restriction enzymes cutting the strands of DNA at specific palindromic sequences. 39 Denaturation- Double-stranded DNA is separated by applying high temperature of oC. 40 Annealing- Primers bind to the 3'ends of the separated DNA strands 41 Extension- DNA polymerase extends the primers by adding complementary nucleotides.Taq polymerase is used here. 42 Taq Polymerase- DNA polymerase obtained from bacteria Thermus aquaticus |
Core Techniques
- Genetic Engineering
- Sterile conditions for culture of the host and collection of products
Recombinant DNA Technology
- Formation of Recombinant DNA: (gene of interest + vector )
- Gene Cloning in the vector (in vivo)
- Gene transfer to host cell for culturing and obtaining the product of the gene
Steps to Create rDNA
- Step 1: Isolation of DNA from the organism by using enymes like lysozyme, chitinase, protease, RNAse and precipitating in chilled ethanol.
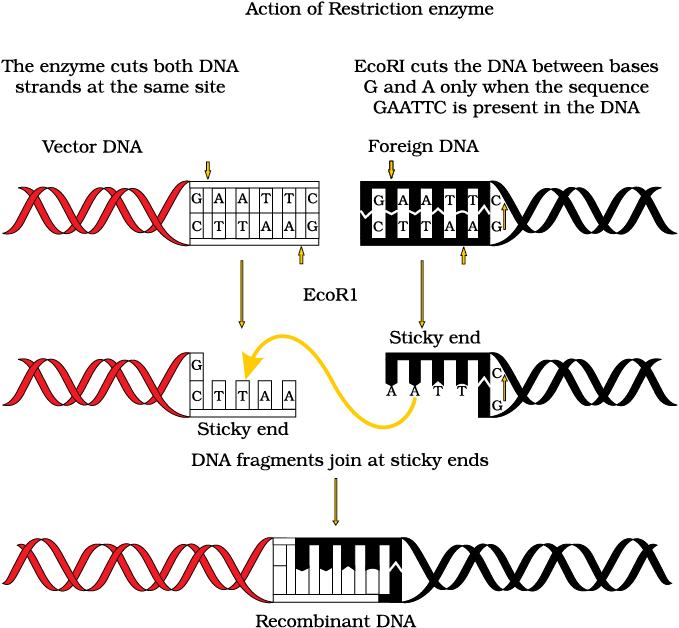
- Step 2: Cutting of DNA at recognition sites by Restriction enzymes .The same enzyme cuts the cloning vector at a similar recognition site producing sticky ends.
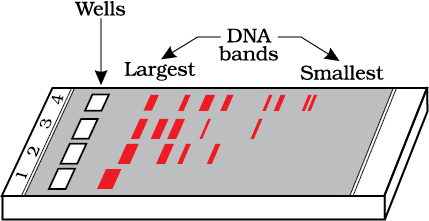
- Step 3: The cut fragment is separated using Gel Electrophoresis and amplified using PCR.
- Step 4: The gene (DNA fragment)is joined with the cloning vector DNA using Ligase.
- Step 5: The recombinant DNA thus formed is transferred into host cell using methods like biolistics, microinjection, or pathogens like bacteria and retroviruses whose pathogenic properties have been removed.
- Step 6: The host cell containing the rDNA is cultured in Bioreactors to produce the product.
- Step 7: The product is separated, purified, (downstream processing) formulated with preservatives followed by quality control testing.
Enzyme Specific Digestion
- Lysozyme to break bacterial cell wall
- Chitinase to break fungal cell wall
- Cellulase to break plant cell wall
- Protease to digest proteins
- RNAse to digest RNA
Restriction Enzymes
- They are Endonucleases
- They specific recognition sites which are palindromic
- These are named after the genus, species and order of isolation from their hostcell
Gel Electrophoresis
- Negatively charged DNA are forced to move through a gel ,towards an anode, in an electric field.
- The smaller fragments sieve through the gel faster and move faster to the anode.
- The larger ones remain near the wells at the cathode end as they sieve slowly.
- The separated fragments are stained with ethidium bromide and visualized under UV light.
- The DNA fragments are cut out from the gel –a process known as Elution.
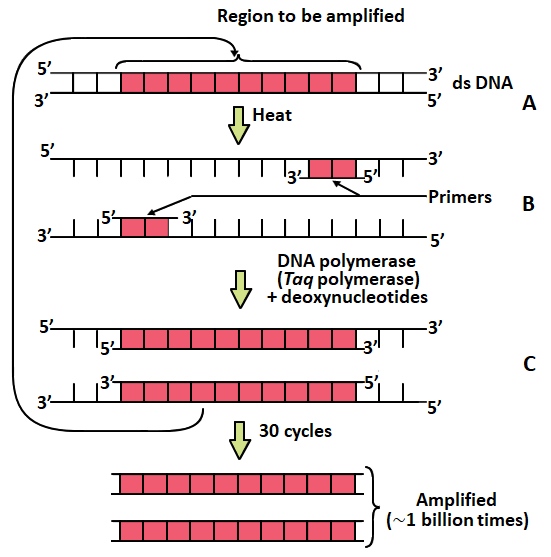
Polymerase Chain Reaction
-
Denaturation of DNA (separation of DNA into single strands)by applying high temperature up to 95 oC.
- Annealing: Two sets of Primers (short stretches of RNA) attach to the single stranded DNA at complementary sites.
- Addition of Taq Polymerase
- Extension: The primers extend by the addition of nucleotides in the presence of thermostable DNA polymerase complementary to the DNA strand. The Primers are removed.
- Repeat: This cycle gets repeated 30 times and the DNA fragment gets amplified about a billion times.
Methods of gene transfer
Vectorless methods
- Direct method –Direct uptake of DNA after treatment with Calcium ions incubation in ice and heat shock treatment. Used for bacteria.
- Biolistics – Used for Plant cells
- Microinjection – Used for Animal cell
Vector method
- Bacteriophages
- Plasmid for Bacteria
- Disarmed pathogen
- Agrobacterium for plants
- Retrovirus for animals
Characteristics of Cloning Vector
- Ori site: Origin of replication. It should be capable of supporting several replications to make many copies.
- Restriction site: For the action of different restriction enzymes where the gene of interest can be inserted
- Selectable Markers: The presence of these genes in the host will help in selecting the host cell which has the gene from the cells which do not carry the genes. The rDNA-carrying cells called transformants can be selected and separated from the non-transformants.
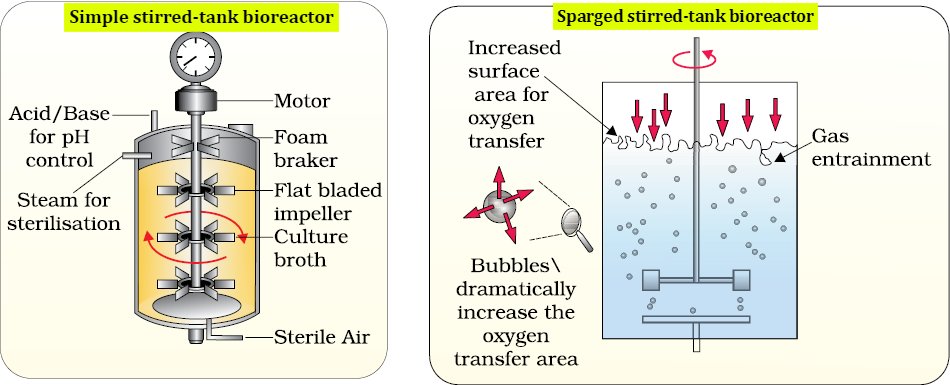
Bioreactors
Produce recombinant protein using raw materials and living cells/enzymes.
- Sparged stirred tank
- Simple stirred tank
| Download CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Biotechnology: Principles and Processes Revision Notes PDF |
Read: NCERT Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter-Wise
Read: CBSE Class 12 Biology Mind Map: All Chapters
Read: CBSE Class 12 Biology Important MCQs for All Chapters
Related:
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers and Marking Schemes 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Revised Textbook PDF
- CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Solutions
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation