The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam 2025 is set for February 27, 2025, and as the exam approaches, strategic revision is crucial for scoring high marks. To assist students in their last-minute preparation, our subject experts have curated a CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 2025, covering important questions aligned with the latest CBSE syllabus and exam pattern. This expert-designed sample paper focuses on high-weightage topics, ensuring a strong conceptual grasp. Download now to enhance your preparation and boost your scores in the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam 2025.
Key Features of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 2025:
- Expert-Designed Paper: Curated by subject experts to ensure comprehensive coverage of important topics.
- Different from CBSE Sample Paper: Provides additional practice beyond the official CBSE sample paper.
- Latest Exam Pattern-Based: Fully aligned with the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2025 syllabus and marking scheme.
- Includes Varied Question Types: Covers MCQs, short-answer, and long-answer questions for complete preparation.
- Downloadable in PDF Format: Available in PDF format for easy access and practice anytime.
- Check and download the sample paper below and give the final touch to your Class 12 Chemistry Exam preparations.
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Sample Paper 2025
Section-A MCQ’s
1. Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose
(b) On heating with HI it forms n-hexane
(c) It is present in pyranose form
(d)It forms an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNP
Answer: (d) It forms an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNP
2. Write the IUPAC name of the product of the following reaction
C₆H₅N₂Cl + H₂O →
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Bromobenzene
(c) p-chlorophenol
(d) Phenol
(d) Phenol
3. Which of the following lanthanoids show a +4 oxidation state besides the characteristic oxidation state +3 of lanthanoids?
(a) Ce
(b) Eu
(c) Tb
(d) Dy
Answer: (a) Ce
4. If 96500-coulomb electricity is passed through CuSO₄ solution, it will liberate (At. Wt of Cu = 63.5 g/mol)
(a) 63.5 g of Cu
(b) 31.75 g of Cu
(c) 127 g of Cu
(d) 100 g of Cu
Answer: (b) 31.75 g of Cu
5. What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?
R—OH + HCl → R—Cl + H₂O
(a) 1° > 2° > 3°
(b) 1° < 2° < 3°
(c) 3° > 2° > 1°
(d) 3° > 1° > 2°
Answer: (c) 3° > 2° > 1°
6. The magnetic nature of elements depends on the presence of unpaired electrons. Identify the configuration of the transition element, which shows the highest magnetic moment.
(a) 3d⁷
(b) 3d⁵
(c) 3d⁸
(d) 3d²
Answer: (b) 3d⁵
7. Which reagent will you use for the following reaction?
CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₃ → CH₃CH₂CH₂CH₂Cl + CH₃CH₂CHClCH₃
(a) Cl₂/UV light
(b) NaCl + H₂SO₄
(c) Cl₂ gas in the presence of Fe in dark
(d) Cl₂ gas in dark
Answer: (a) Cl₂/UV light
8. Which of the following pairs of ions have the same electronic configuration?
(a) Cu²⁺, Cr²⁺
(b) Fe³⁺, Mn²⁺
(c) Co³⁺, Ni³⁺
(d) Sc³⁺, Cr³⁺
Answer: (b) Fe³⁺, Mn²⁺
9. Phenol is less acidic than:
(a) Ethanol
(b) o-nitrophenol
(c) o-methyl phenol
(d) o-methoxy phenol
Answer: (b) o-nitrophenol
10. A tertiary alcohol is obtained by the reaction of Grignard reagent with:
(a) Butanone
(b) Propanone
(c) Acetone
(d) All of the above
Answer: (d) All of the above
11. The IUPAC name of CH₃-CH=CH-CHO is:
(a) Buten-2-al
(b) Butenal
(c) But-2-enol
(d) But-2-enal
Answer: (d) But-2-enal
12. An organic compound X on treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate in dichloromethane gives compound Y. Compound Y reacts with I₂ and alkali to form triiodo methane. The compound ‘X’ is:
(a) CH₃CH₂OH
(b) CH₃CHO
(c) CH₃COCH₃
(d) CH₃COOH
Answer: (a) CH₃CH₂OH
For question number 13 to 16 two statements labelled Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
13. Assertion: The conductivity of a solution decreases with a decrease in concentration.
Reason: The number of ions per unit volume of solution decreases.
Answer: (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
14. Assertion: D(+)Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Answer: (c) A is true but R is false.
15. Assertion: Aryl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions more easily.
Reason: The carbon-halogen bond in aryl halides has a partial double bond character.
Answer: (d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
16. Assertion: Sodium hydrogen sulphite adds to aldehydes and ketones to form the addition product.
Reason: The reaction of aldehydes with Sodium hydrogen sulphite is useful for the separation and purification of aldehydes.
Answer: (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Also, check: CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Top 50 MCQs For Board Exam 2025
Section- B Very Short Answer Questions
This section contains 5 questions with internal choice in one question. The following questions are very short answer types and carry 2 marks each.
17.(a) Define molality.
(b) Give an example of a Solid-Solid solution.
Answer: (a) Number of moles of solute dissolved per kilogram of solvent/ any suitable definition
(b) Copper and Gold / any suitable example
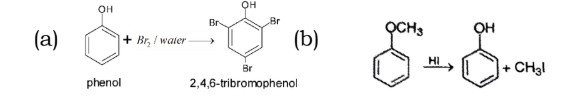
18. What happens when
(i) Phenol reacts with bromine water?
(ii) Anisole reacts with HI?
Write the chemical equations involved in the above reactions.
19. Name the nitrogenous bases present in RNA. Which one of these is not present in DNA?
Answer: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. (if all bases are correct 1 mark)
uracil
20. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of property mentioned within brackets.
(a) CH₃CHO, CH₃CH₂OH, CH₃OCH₃, CH₃CH₂CH₃ (boiling point)
(b) Ethanol, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone (reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction)
Answer: (a) CH3CH2CH3 < CH3OCH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH
(b) Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal
21. A first-order reaction has a rate constant of 1.15 × 10⁻³ s⁻¹. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3g?
(log 5 = 0.6990 , log 3 = 0.4771)
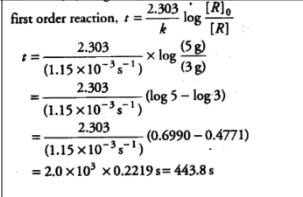
Section-C- Short Answer Questions
22. When a certain conductivity cell was filled with 0.1 M KCl, it has a resistance of 85 ohms at 25°C. When the same cell was filled with an aqueous solution of 0.052 M unknown electrolyte, the resistance was 96 ohms. Calculate the molar conductivity of the electrolyte at this concentration. Conductivity of 0.1 M KCl = 1.29 × 10⁻²Ω⁻¹cm⁻¹.
Answer:

23. Write the formula of the following coordination compound:
- Iron(III)hexacyanoferrate(II).
What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4[Co(NH₃)₅Cl]SO₄[Co(NH3)5Cl]SO4?
Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex [CoF6]3−[CoF₆]³⁻[CoF6]3−. (Atomic Number of Co =27)
OR
(i) What is meant by crystal field splitting energy?
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms of t2g and eg in an octahedral field when
(a) Δ0>P
(b) Δ0<P
Answer:

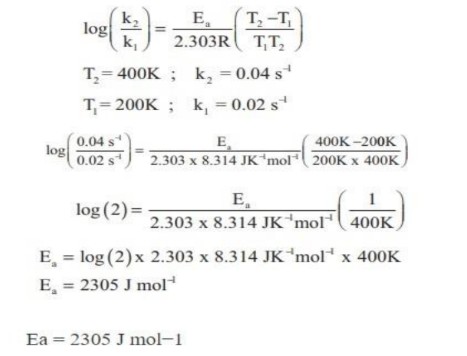
24. The rate constant of a reaction at 400K and 200K are 0.04 and 0.02 s⁻¹ respectively. Calculate the value of activation energy.
(log2 = 0.3010; R = 8.314 JK⁻¹mol⁻¹)
Answer:
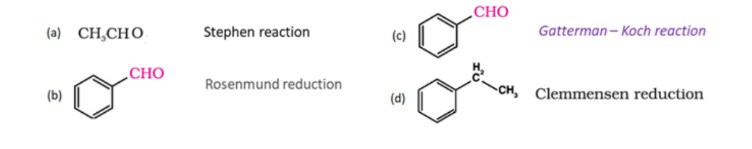
25. Below, reactants of some organic name reactions are given. Write the structure of the main product in each and also identify the name reaction.
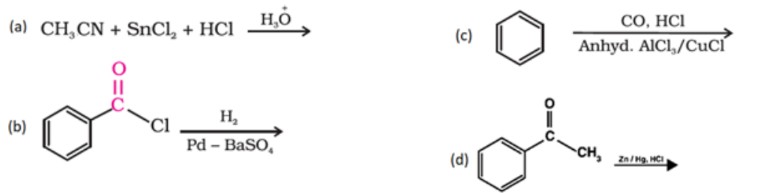
(i) CH₃CN + SnCl₂ + HCl →
(ii) Pd – BaSO₄
(iii) Anhyd. AlCl₃/CuCl
(iv) CO, HCl
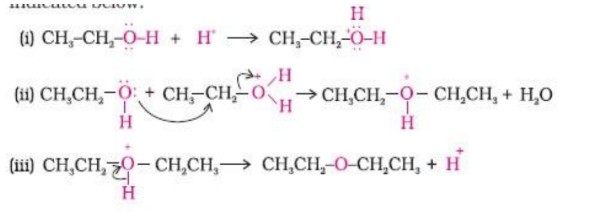
26. Write the mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethoxyethane.
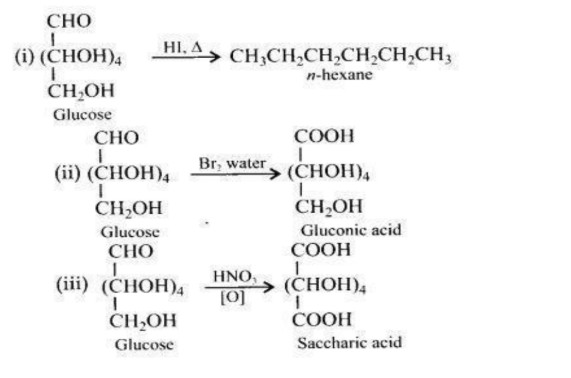
27. What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents?
(i) HI
(ii) Bromine water
(iii) HNO₃
28. Compound ‘A’ with molecular formula C4H9Br is treated with aq. KOH solution. The rate of this reaction depends upon the concentration of the compound ‘A’ only. When another isomer ‘B’ of this compound was treated with aq. KOH solution, the rate of reaction was found to be dependent on the concentration of the compound and KOH.
(i) Write down the structural formula of both the compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’.
(ii) Out of these two compounds, which one will be optically active?
Answer: i. A is 1-Bromo butane and B is 2-Bromo butane.
ii. B is optically active.
Section-D- Case-Based Questions
The following questions are case-based questions. Each question has an internal choice and carries 4 (1+1+2) marks each. Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
29. Coordination compounds contain a metallic element as the central atom and are therefore referred to as metal complexes. These types of coordination complexes generally consist of a transition element as the central atom. It can be noted that the central atom in these complexes is called the coordination centre. A chemical compound in which the central ion or atom (or the coordination centre) is bound to a set number of atoms, molecules, or ions is called a coordination entity. Some examples of such coordination entities include [CoCl₂(NH₃)₄] and [Fe(CN)₆]³⁻.
In coordination compounds, the central atoms or ions are typically Lewis acids and can, therefore, act as electron-pair acceptors. The atoms, molecules, or ions that are bound to the coordination centre or the central atom/ion are referred to as ligands. These ligands can either be a simple ion or molecule, such as Cl⁻ or NH₃ or in the form of relatively large molecules, such as ethane-1,2-diamine (NH₂-CH₂-CH₂-NH₂). The coordination sphere is the non-ionizable part of a complex compound, which consists of a central transition metal ion surrounded by neighbouring atoms or groups enclosed in a square bracket.
(a) Write down the formula of Tetraammineaquachloridocobalt(III) chloride.
(b) Calculate the coordination number of Co in [Co(en)₃]³⁺.
(c) Give a chemical test to distinguish between [Co(NH₃)₅Br]SO₄ and [Co(NH₃)₅SO₄]Br.
Or
Describe the shape and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺. (Atomic no. of Cu = 29)
Answer 29:

30. Electricity can be produced when electrons move from one element to another in certain types of reactions (such as redox reactions). Typically, electrochemistry deals with the overall reactions when multiple redox reactions occur simultaneously, connected via some external electric current and a suitable electrolyte. In other words, electrochemistry is also concerned with chemical phenomena that involve charge separation (as seen commonly in liquids such as solutions). The dissociation of charge often involves charge transfer that occurs homogeneously or heterogeneously between different chemical species. A spontaneous chemical process is one that can take place on its own, and in such a process, the Gibbs free energy of a system decreases. In electrochemistry, spontaneous reaction (redox reaction) results in the conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy. The reverse process is also possible where a non-spontaneous chemical reaction occurs by supplying electricity. These interconversions are carried out in equipment called an electrochemical cell.
(a) Name the electrochemical cell generally used in hearing aids.
(b) Λm of CH₃COOH increases drastically, while that of CH₃COONa increases gradually on dilution. Explain.
Or
Can copper sulphate solution be stored in a zinc pot? Explain.
(E° Zn²⁺/Zn = -0.76V, E° Cu²⁺/Cu = 0.34V)
(c) The standard electrode potential for the Daniell cell is 1.1 V. Calculate the standard Gibbs energy for the cell reaction. (F = 96,500 C mol⁻¹)
Answer 30:

Section-E: Long answer type questions
31. (a) Complete the following ionic equations:
i) Cr₂O₇²⁻ (aq) + I⁻ (aq) + H⁺ (aq) →
ii) Fe²⁺ (aq) + MnO₄⁻ (aq) + H⁺ (aq) →
(b) Explain the following observations:
i) In general, the atomic radii of transition elements decrease with atomic number in a given series.
ii) The E° value for Cu²⁺/Cu is positive (+0.34 V). It is the only metal in the first series of transition elements showing this type of behaviour.
iii) The E° value for Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺ couple is much more positive than for Cr³⁺/Cr²⁺ or Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺ couple.
OR
Assign reasons for the following:
a) The enthalpies of atomization of transition elements are high.
b) Transition metals and many of their compounds act as good catalysts.
c) E°(M²⁺/M) values are not regular for first-row transition metals (3d series).
d) Although F is more electronegative than O, the highest Mn fluoride is MnF₄, whereas the highest oxide is Mn₂O₇.
e) Sc³⁺ is colourless in an aqueous solution, whereas Ti³⁺ is coloured.
Answer 31:
(a) i) 5Fe²⁺ (aq) + MnO₄⁻ (aq) + 8H⁺ (aq) → Mn²⁺ (aq) + 5Fe³⁺ (aq) + 4H₂O(l)
ii) Cr₂O₇²⁻ (aq) + 6Fe²⁺ (aq) + 14H⁺ (aq) → 2Cr³⁺(aq) + 3Fe³⁺ (aq) + 7H₂O(l)
(b) i) Because of the increase in effective nuclear charge and the weak shielding effect of d electrons, the atomic radii decrease.
ii) It is because Copper has a high enthalpy of atomization and low enthalpy of hydration. The high energy required to transform Cu(s) to Cu²⁺(aq) is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy.
iii)The large positive E° value for Mn³⁺/Mn²⁺ shows that Mn³⁺ is much more stable than Mn²⁺ due to stable half-filled configuration (3d⁵). Therefore the 3rd ionization energy of Mn will be very high and Mn³⁺ is unstable and can be easily reduced to Mn²⁺. E° value for Fe³⁺/Fe²⁺ is positive but smaller i.e. Fe³⁺ can also be reduced to Fe²⁺ but less easily. Thus Fe³⁺ is more stable than Mn³⁺.
OR
(a) This is because transition elements have strong metallic bonds as they have a large number of unpaired electrons, therefore they have greater interatomic overlap.
(b) The catalytic activity of transition metals is attributed to the following reasons
i) Because of their variable oxidation state, transition metals form unstable intermediate compounds and provide a new path with lower activation energy for the reaction.
ii) In some cases, the transition metal provides a suitable large surface area on which the reactants are adsorbed.
(c) E°(M²⁺/M) values are not regular in the first transition series metals because of irregular variation of ionization enthalpies (IE₁ & IE₂) and sublimation energies.
(d) Among transition elements, the bonds formed in +2 and +3 oxidation states are mostly ionic. The compounds formed in higher oxidation states are generally formed by sharing of d-electrons. Therefore, Mn can form MnO₄⁻ while fluorine cannot form multiple bonds.
(e) Number of unpaired d-electrons in Sc³⁺ whereas in Ti³⁺ there is one unpaired electron or Ti³⁺ shows the d-d transition.
32. A colourless substance ‘A’ (C₆H₇N) is sparingly soluble in water and gives a water-soluble compound ‘B’ on treatment with HCl. On reaction with CHCl₃ and alcoholic KOH, ‘A’ produces an obnoxious smell due to the formation of compound ‘C’. The reaction of ‘A’ with benzene sulphonyl chloride gives compound ‘D’ which is soluble in alkali. ‘A’ reacts with NaNO₂ and HCl, to form compound ‘E’. Identify compounds ‘A’ to ‘E’.
OR
(a) Why is benzene diazonium chloride not stored and used immediately after its preparation?
(b) Explain why MeNH₂ is a stronger base than MeOH.
(c) What is the role of pyridine in the acylation reaction of amines?
(d) Give one chemical test to distinguish between Aniline and benzylamine.
(e) Give a suitable reaction to convert aniline to bromobenzene, name the reaction also.
Answer 32:
A = C₆H₅NH₂
B = C₆H₅NH₃⁺Cl⁻
C = C₆H₅NC
D = N-phenylbenzenesulphonamide
E = C₆H₅N₂⁺Cl⁻
OR
a) Benzene diazonium chloride cannot be stored and is used immediately after its preparation because of its unstable nature. With a slight increase in temperature, it dissociates to give nitrogen gas.
b) Nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen; therefore, lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen are readily available for donation. Hence, MeNH₂ is more basic than MeOH.
c) Pyridine acts as an acceptor for the acid by-product formed in the reaction. Thus, it removes the side product, i.e. HCl, from the reaction mixture.
d) Azo dye Test
e) Step 1. Diazotization and step 2. Sandmeyer/Gattermann reaction
![]()
33. (i) Define the following terms:
(a) Azeotrope
(b) Osmotic pressure
(c) Colligative properties
(ii) Calculate the molarity of 9.8% (w/w) solution of H₂SO₄ if the density of the solution is 1.02 g mL⁻¹. (Molar mass of H₂SO₄ = 98 g mol⁻¹)
OR
(i) On mixing liquid X and liquid Y, the volume of the resulting solution decreases. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law is shown by the resulting solution? What change in temperature would you observe after mixing liquids X and Y?
(ii) What happens when we place the blood cell in water (hypotonic solution)? Give reason.
(iii) At 25°C the saturated vapor pressure of water is 3.165 kPa (23.75 mm Hg). Find the saturated vapour pressure of a 5% aqueous solution of urea (carbamide) at the same temperature. (Molar mass of urea = 60.05 g mol⁻¹)
Answer 33:
(i) (a) The binary mixtures of liquids having the same composition in liquid and vapour phase and boiling at a constant temperature are called azeotropes.
(b) The excess pressure which must be applied to the solution side to prevent the passage of solvent into it through a semipermeable membrane is called osmotic pressure.
(c) The properties of solutions which depend only on the number of solute particles in the solution but are independent of their nature are called colligative properties.

Also, get the links to the questions and answer below:
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Sample Paper 2025 By Experts With Solutions FREE PDF Download |
Other Related Links
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation