CBSE Class 12th Economics Board Exam 2025: The CBSE Class 12 Economics Standard exam is scheduled for March 19, 2025. Economics, as an important subject, plays a major role in boosting overall board exam scores. To help students prepare effectively, we provide the CBSE Class 12 Economics Sample Paper with Solutions. Designed by experts, this resource is ideal for last-minute revision and practising important questions. The solutions offer clarity on correct answers. Download the CBSE Class 12 Economics Paper PDF from the links below to strengthen your preparation and score well in the exam.
Check:
| CBSE Class 12 Economics Syllabus 2024-25 |
Prominent Features of CBSE Class 12 Economics Sample Paper 2025
- Prepared by Experienced Faculty – Designed by subject experts to ensure quality and accuracy.
- Based on the Latest Syllabus and Exam Pattern – Aligned with the CBSE Class 12 Economics syllabus for 2025.
- Includes Important Questions – A valuable resource for practicing key topics and question types.
- Offers Additional Questions – Provides a variety of questions beyond those in the CBSE-issued sample paper.
- Comes with Solutions – Facilitates quick and effective revision by providing well-structured answers.
- Available in PDF Format – Easily downloadable for convenient access and offline practice.
Also Check: CBSE Class 12 Economics Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme 2025
CBSE Class 12 Economics Sample Paper 2025 with Solutions
Check and download the Class 12 Economics Sample Paper with Solutions to Boost your preparation for the upcoming CBSE Class 12 Economics Exam 2025:
GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS:
1.This question paper contains two sections:
Section A – Macro Economics
Section B – Indian Economic Development
2. This paper contains 20 Multiple Choice Questions of 1 mark each.
3. This paper contains 4 Short Answer Questions of 3 marks each to be answered in 60 to 80 words.
4. This paper contains 6 Short Answer Questions of 4 marks each to be answered in 80 to 100 words.
5. This paper contains 4 Long Answer Questions of 6 marks each to be answered in 100 to 150 words.
SECTION A – (Macro Economics)
1.Suppose in an economy, the initial deposits of ₹ 400 crores lead to the creation of total deposits worth ₹ 4000 crores. Under the given situation the value of reserve requirements would be________ (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
a) 0.01
b) 1
c) 0.1
d) 0.4
Ans: c) 0.1 (4000=400 x1/LRR)
2. Inventory is a ...................concept whereas the change in inventory is a ...................... concept. (Fill up the blank with correct alternative)
a) stock, flow b) stock, stock
c) flow, stock d) flow, flow
Ans: a) stock, flow
3. Read the following statement -Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct alternatives given below:
Assertion (A): Saving curve makes a negative intercept on the vertical axis at zero level of income.
Reason (R): Saving function refers to the functional relationship between saving and income.
Alternatives:
a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A
4. “The World Bank has been extending loans to Country X on favourable terms for infrastructure, poverty alleviation, and rural development projects for four decades.” Identify the reason for these loans to be listed as external assistance under the capital account of the Balance of Payments.
a) The loans have been taken from an entity outside the country.
b) The loans aim to improve the standard of living in the country
c) The loans have crossed the three-decade period.
d)The loans can be paid off over a longer period.
Ans: b) The loans aim to improve the living conditions in the country.
5. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
Statement 1 – Public goods are those goods and services that are collectively
consumed by the public.
Statement 2 – Public goods are excludable and rivalrous in nature.
Alternatives:
a) Both the statements are true.
b) Both the statements are false.
c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
d) Statement 2 is true and Statement 1 is false
Ans: c) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false
6. As the Marginal Propensity to Save (MPS) increases, the value of the investment multiplier ____________. (Choose the correct alternative)
a) increases b) does not change c) becomes zero d) decreases
Ans: d) decreases
7. A Bengaluru based company receives a loan from a company situated in Japan. How is this transaction recorded in India’s Balance of Payments account?
(a) Credit side of current account
(b) Debit side of current account
(c) Credit side of capital account
(d) Debit side of capital account
Ans: ( c ) Credit side of capital account
8. Which one of following is not a function of the Reserve bank of India?
(a) Issue of currency
(b) Banker to the public
(c) Banker to Government
(d) Controller of money supply
Ans: (b) Banker to the public
9. Which of the following institution (s) perform the activity of credit creation?
(a) Commercial banks
(b) Central bank
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these:
Ans: (a ) Commercial banks
10. Read the following statements – Assertion (A) & reason (R) carefully & choose
the correct alternative:
Assertion (A): MPC represents the slope of the consumption function.
Reason (R): MPC represents change in consumption due to a given change in income.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation for Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation for Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true.
Ans: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct
explanation for Assertion (A).
11. ‘During the last few years’ initiatives such as Jan Dhan Yojna, Aadhar-enabled payment systems, e-Wallets,National Financial Switch (NFS) and others have strengthened the government's resolve to go cashless.’ Source: NCERT Elaborate on how such initiatives may have affected the Indian economy.
Ans: These initiatives affect the economy by : Increasing the total number of bank deposits. Leading to more deposition of money. Lending capacity of banks increases due to more accounts. Easing of payments systems. Availability of loans, investments increase. All these lead to more pumping of money into the economy leading to the overall growth in the National Income.
12. Study the table given below which has information about two firms of an economy. Wages (in ₹) Profits (in ₹) Interest (in ₹) Rent (in ₹)
Firm A 50 150 100 100
Firm B 90 21 100 100
Further, it should be noted that1. Net Factor Income from Abroad is (-) ₹ 20
2. Employee's contribution to the Social Security Fund by Firm A and Firm B is ₹ 5 and ₹ 10
respectively
Calculate the National Income.
Ans: NDP (factor cost) = 50 + 150 + 90 + 210 + 100 + 100 + 100 + 100 = Rs. 900 National
Income = Net National Product (factor cost) = Net Domestic Product (factor cost) + Net
Factor Income from Abroad NI = NNP (factor cost) = 900 + (-) 20 = Rs. 880
13. a) When does a Current Account Surplus situation arise?
b) Discuss its significance in an economy.
Ans: a) Trade - exports > imports Receipts > payments Employment - higher employment opportunities since there is an increased demand for domestic goods Investments - increased domestic and foreign investments than other countries since the country is exporting more.
b) More competitive market, advanced technology, optimum utilization of resources. Appreciation on the value of the currency.
14. Distinguish between Autonomous and accommodating transactions in balance
of payments accounts.
| Basis | Autonomous Items | Accommodating Items |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic transactions that take place due to economic motives, mainly profit maximization. | Transactions that are not related to profit maximization but help in balancing international accounts. |
| Nature | Determined by business and trade decisions. | Determined by the need to correct imbalances in the balance of payments. |
| Accounts Involved | Take place in both current account and capital account. | Take place only in the capital account. |
| Alternative Name | Known as "Above the Line Items". | Known as "Below the Line Items". |
This classification helps in understanding how international transactions impact the Balance of Payments (BoP), distinguishing between transactions driven by trade and those aimed at maintaining financial stability.
Or
What is foreign exchange rate? Distinguish between fixed and flexible exchange rates.
Ans: The rate, at which currency of one country is converted into currency of the country, is called foreign exchange rate. Fixed exchange rate- Fixed exchange rate system refers to the system in which the rate of exchange for a currency is fixed by the government. Under this system, government is responsible to stabilise the exchange rate. Flexible exchange rate system -refers to a system exchange rate between currencies of different countries is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
15. “Monetary measures offer a valid solution to the problem of inflationary gap in an economy”. State and discuss any two monetary measures to justify to given statement.
Ans: (a)Two monetary measures which may be used to solve the problem of inflation are: (a) As increase in Cash reserve ratio (CRR) – it will reduce credit creation capacity of commercial bank as a result AD falls and correct the inflationary gap in the economy.
(b) Sale of govt securities in open market - By selling government securities the central bank absorbs liquidity from the economy. As a result AD may falls and correct the inflationary gap in the economy.
16. Discuss any one of the following functions of a central bank:
(a) As government bank
(b) Open market operations
(a) The central bank acts as the banker to the government, maintain accounts of government for the purpose of accepting deposits and advancing loans. The Central bank purchases and sells govt securities in the open market operations on behalf of the govt.
(b) Open market operations (OMO) -refers to buying and selling of government securities (bonds) by the central bank from /to the general public. By selling government securities the central bank soak liquidity from the economy. By purchasing government securities the central bank releases liquidity in the economy.
Or
Assuming that initial deposit with bank ₹5000 Crore legal reserve ratio 10% , Explain the process of credit creation by the bank.
Ans: Working of credit creation process : Total credit = initial deposits ×1/ LRR Initially, customer deposits ₹ 5,000 and LRR is 10 % . Bank keeps ₹ 500 reserves to meet customers’ obligations and give loans of ₹ 4500. Those who borrow will spend this money and same ₹ 4500 will ultimately come back to bank as fresh deposits .And this process goes continuously until initial deposits becomes equals to total reserves. Credit creation process is give below:
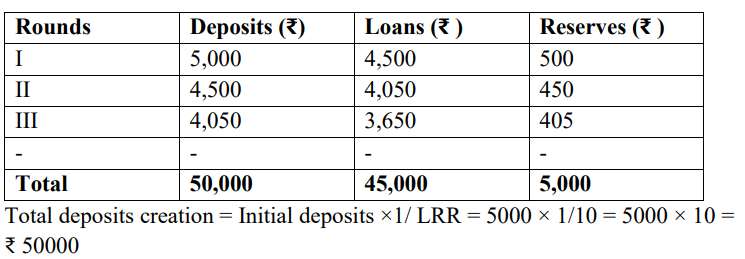
17. Identify the following as Revenue expenditure or capital expenditure. Give reason
(i) Salary paid to government employee
(ii) Purchase of machine from Korea.
(iii) Repayment of loan taken from IMF.
(iv) Interest paid on national debt.
(v) Expenditure on construction of dam.
(vi) Social security benefits paid to retired government employee.
Ans: (a) It is revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government.
(b) It is a capital expenditure as it increases assets of the government.
(c) It is a capital expenditure as it reduces liability of the government.
(d) It is revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government.
(e) It is a capital expenditure as it increases assets of the government.
(f) It is revenue expenditure as it neither creates any asset nor reduces any liability of the government.
Or
(A)Elaborate the objective of ‘allocation of resources’ in the government budget.
(B) Distinguish between revenue receipts and capital receipts of the government, with suitable examples.
Ans: (a) It refers to change in direction of resources from one use to other. The govt seeks to re allocate resources with a view to balance the goals of profit maximisation and social welfare. Unlink private enterprises, govt targets social welfare also along with profit motive. Production of goods which are injurious to health is discouraged through heavy taxation. on the other hand, production of socially useful goods is encouraged through subsidies.
(b) Revenue receipts are those receipts of govt during the fiscal years which do not affect asset or liability status of the government. Example tax receipts, nontax receipts. Capital receipts are those receipts which create liability for government and reduce govt asset. Example borrowings, disinvestment, recovery of loan.
SECTION- B (Indian Economic Development)
18. Details about the population of British India were first collected in :
(a) 1871 (b) 1881 (c) 1891 (d) 1901
Ans: (b) 1881
19. In the Industrial Policy Resolution of 1956, industries were classified in ……………. Categories.
(a) Two (b) three (c) four (d) five
Ans: (c) three
Or
In 1955, Karve committee was constituted for aiming the ……………..
(a) Modernization (b) Industrial development
(c) Development of small scale industries (d) Self-reliance
Ans: (c ) Development of small scale industries
20. Introduction of Economic Reforms in China took place in the year………..
(a) 1978 (b) 1980 (C ) 1988 (d) 1991
Ans: (a ) 1978
Or
Arrange the following events in chronological order and choose the correct
answer from the given alternatives:
(i) Establishment of People’s Republic of China.
(ii) Creation of Pakistan
(iii) First Five-Year Plan of India.
(iv) First Five-year Plan of China.
(a) (i), (iv), (ii), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (i), (iv)
(c) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
(d) (iv), (iii), (ii), (i)
Ans: ( c) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
21. National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was set up in :
(a) 1980 (b) 1981 ( c) 1982 (d) 1983
Ans: ( c) 1982
22. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative:
Statement-I: Human capital is not sold in the market; only the services of the human capital are sold.
Statement-II: Human capital is perfectly mobile between countries.
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false.
(d) Statement-II is true, Statement -I is false.
Ans: (C) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false.
23. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct alternative:
Statement-I: while India and Pakistan became independent nations in 1947, People’s Republic of China was established in 1949.
Statement-II: while India announced its first Five Year Plan in 1951, Pakistan announced its first five-year plan, now called the Medium-Term Development Plan, in 1953. China announced its First Five Year Plan in 1956.
(a) Both the statements are true.
(b) Both the statements are false.
(c) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false.
(d) Statement-II is true, Statement-I is false.
Ans: (C) Statement-I is true, Statement-II is false.
24. Identify the result of the large export surplus during the colonial period.
(a) domestic markets flooded with raw materials
(b) an increase in gold and silver reserves
(c) scarcity of essential commodities
(d) cheap imported consumer goods
Ans: c) scarcity of essential commodities
other question will be updating soon...
Also Check:
CBSE Class 12 Economics Sample Paper and Marking Scheme 2024-25
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation