This topic explores the difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions in chemistry. Chemical reactions encompass a variety of processes categorised into subgroups, including endothermic and exothermic reactions, which release energy in forms such as sound, light, cold, or heat. Basically, endothermic reactions absorb heat energy from their surroundings, whereas exothermic reactions release energy into their surroundings.
Image: Adobe Stock
Endothermic Reactions
The endothermic process refers to reactions where the system absorbs heat energy from its surroundings. The term "Endo" signifies "to absorb," and "thermic" pertains to "heat." Energy is absorbed during these reactions as bonds between molecules break in the reactants. This absorbed energy is then released when new bonds form in the products. During endothermic reactions, heat is absorbed from the surroundings, resulting in a decrease in the temperature of the system where the reaction occurs. At the conclusion of the reaction, the enthalpy change, which represents the heat energy change during the transformation from reactants to products, increases.
Exothermic Reactions
An exothermic reaction releases energy in the form of light or heat to its surroundings, contrasting with endothermic reactions which absorb energy. The term "Exo" denotes "release," and "thermic" refers to "heat." Energy is released because new bonds form at a lower energy level than the bonds in the reactants. Breaking the bonds in the reactants requires less energy. Consequently, the overall enthalpy change decreases during the reaction. Chemical reactions involve significant energy. This energy is initially used to maintain the bonds within molecules. When molecules and compounds react, breaking bonds releases a substantial amount of energy.
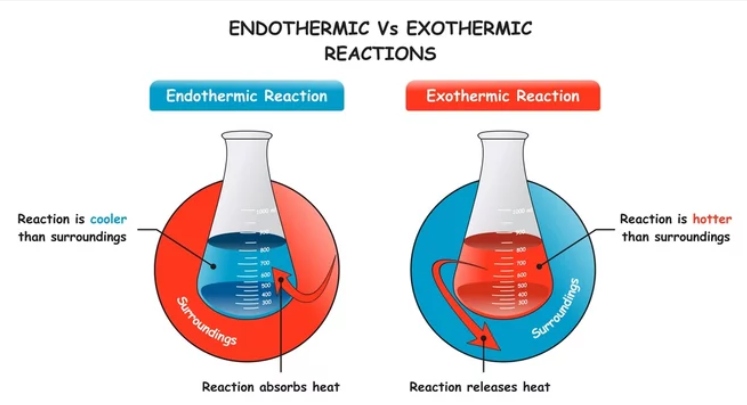
Image: Adobe Stock
Difference between Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions
Find the table with the feature and the difference between Endothermic Reaction and Exothermic Reaction:
| Feature | Endothermic Reaction | Exothermic Reaction |
| Heat Flow | Absorbs heat | Releases heat |
| Energy Change (ΔH) | Positive (+) | Negative (-) |
| Temperature Change | Decreases | Increases |
| Bonding | Forming bonds (energy input) | Breaking bonds (energy released) |
| Example | Dissolving ammonium nitrate in water | Burning wood |
Related Video Lessons Link For Students
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation