The JEE Main 2025 Session 1 admit card has been released, and it’s time for students to understand how their percentile and rank will be calculated by the National Testing Agency (NTA). Basically, the JEE Main percentile represents the percentage of candidates who scored lower than a particular candidate. However, the NTA uses a unique method to calculate the JEE Main Percentile Score for 2025.
For JEE Main 2025, the percentile is calculated separately for each subject: Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics. The highest possible percentile is 100, and it is calculated up to seven decimal places to ensure that no two candidates are tied for the same position. This is crucial as it helps avoid conflicts while allocating seats. Understanding this process will help students navigate how their percentile translates to rank, which plays a critical role in the admission process.
Check: JEE Main 2025 Admit Card 2025: Direct Active Link
What is the JEE Main 2025 Percentile Score?
The JEE percentile score compares your performance with other test takers. It is different from a percentage score or raw marks. The percentile score shows the percentage of candidates who scored equal to or lower than you in the exam. While it can be helpful to estimate your rank before the official results are out, it's important to understand the normalization process and the tiebreaker rules used to calculate the JEE Main marks and percentiles.
Syllabus:
- JEE Main 2025 Physics Syllabus With Topic Wise Weightage
- JEE Main 2025 Maths Syllabus With Topic Wise Weightage
- JEE Main 2025 Chapter-Wise Weightage
JEE Main Rank vs Percentile Key Difference
Here’s a key difference between JEE Main Rank and Percentile in a concise tabular format:
Aspect | JEE Main Rank | JEE Main Percentile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indicates your exact position among all candidates based on score. | Indicates how well you performed relative to other candidates. |
| What it reflects | Absolute position in the competition (lower rank = better performance). | Relative performance compared to others (higher percentile = better performance). |
| Calculated From | Your raw score in JEE Main exam. | Your rank relative to all candidates; based on normalization. |
| Range | The rank is a number, usually ranging from 1 to several lakhs depending on the performance. | The percentile is a number between 0 and 100, indicating the percentage of students you performed better than. |
| Interpretation | A lower rank means a better performance. | A higher percentile indicates a better performance compared to more candidates. |
| Use for Admission | Directly determines eligibility for admission to various institutes. | Helps to understand how you performed relative to others but is converted to rank for admission. |
| Example | Rank 500 means you're the 500th best student. | A percentile of 99 means you performed better than 99% of students. |
| Impact of Normalization | Ranks are influenced by raw scores and number of candidates. | Percentiles are based on the overall distribution across different sessions of the exam. |
Related | 10 Best Engineering Institutes in India other than IITs, NITs and IIITs
JEE Main Rank Vs Percentile
The relationship between JEE Main Rank and Percentile is crucial to understand how your performance compares to others in the exam. Here’s a detailed comparison of how the two metrics correspond to each other:
1. Percentile:
- The percentile reflects your relative performance compared to all other candidates who appeared for the exam.
- A higher percentile means your performance is better than a larger percentage of candidates.
- Formula for Percentile:
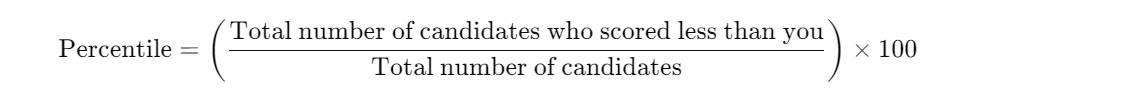
Check: JEE Main 2025 Syllabus
2. JEE Main Rank:
- The rank shows your actual or exact position in the competition.
- Lower the rank means better performance.
- The rank is derived from the percentile, so a higher percentile results in a lower rank.
JEE Main Rank vs Percentile: Approximate Range
Below is an approximate range to understand the relationship between your percentile and rank in JEE Main:
Percentile | Estimated Rank Range |
|---|---|
| 100 Percentile | Rank 1 (Top performer) |
| 99.9 Percentile | Rank 50 - 100 |
| 99 Percentile | Rank 500 - 1000 |
| 98 Percentile | Rank 1000 - 2000 |
| 95 Percentile | Rank 3000 - 5000 |
| 90 Percentile | Rank 5000 - 8000 |
| 85 Percentile | Rank 8000 - 12000 |
| 80 Percentile | Rank 12000 - 15000 |
Check: City Intimation Slip
Key Points:
- 100 Percentile: Means you're the highest scorer, often tied between the top candidates.
- 99 Percentile: This generally translates to being within the top 1% of all candidates, often resulting in ranks between 500-1000.
- 95 Percentile: It indicates you scored better than 95% of candidates, which may give you a rank between 3000-5000.
- Lower Percentiles: As the percentile decreases, the rank number increases, meaning the student’s performance is lower relative to others.
Check | JEE Main 2025 Chapter-Wise Weightage
Factors Influencing Rank:
- Since JEE Main is held in multiple sessions, the percentile is normalized across all sessions, which helps in ensuring fairness. This might slightly vary the exact rank for different sessions.
- The overall rank distribution also depends on the total number of candidates who appear in the JEE Main exam.
Final Remarks:
- A higher percentile means you performed well relative to others, but your rank is what determines your eligibility for admission to different IITs, NITs, and other institutes.
- Always aim for the highest percentile possible to secure a low rank and better admission chances to top institutions.
Steps for Finding Percentile Ranks
To calculate your percentile rank, you need to compare your performance to others in the exam. Below are the steps to find your percentile rank:
Step 1: 🡻
| Organize Data Matrix | What is the first operation that must be performed in an effort to find percentile ranks? Construct a solution matrix |
Step 2: 🡻
| X | What is the raw value or score for which you wish to calculate a percentile rank (PR)? The value may be any value which occurs within the distribution. It must be a whole number. |
Step 3: 🡻
| c% | What is the cumulative percentage of all the values below the critical interval? cf÷n. Add the frequencies and divide by the total number of values in the distribution. |
Step 4:🡻
| L | What is the real lower limit (L) of the critical interval? This is the lowest value that can be included in the interval in which X is located. |
Step 5:🡻
| i | What is the size or width of the critical interval? The size is determined by subtracting the lower limit of the interval from the upper limit (U-L). |
Step 6: 🡻
| f/n(100) | What is the frequency of values in the critical interval divided by the total number of values and multiplied by 100? The result is the percentage of the values in the critical interval |
Step 7: 🡻
| Mathematical Computation | Substitute the appropriate values within the formula and solve. |
Step 8: 🡻
| Conclusions | Draw conclusions based on the final result of your data analysis. |
Also Check:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation