Kirchhoff's Laws quantify how current flows through a circuit and how voltage varies around a loop in a circuit. These include two fundamental principles that govern the behaviour of electrical circuits. They were formulated by German physicist Gustav Kirchhoff in 1845 and are essential for analyzing currents and voltages within a circuit.
Kirchhoff's Current Law (1st Law)
- It states that the total current entering a junction (meeting point of conductors) in a circuit is equal to the total current leaving the junction.
- This principle reflects the conservation of charge, meaning charge cannot disappear or be created within the circuit.
- It is also known as Kirchhoff's First Law or the Junction Rule.
Kirchhoff's Current Law Formula
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
ΣIin = ΣIout
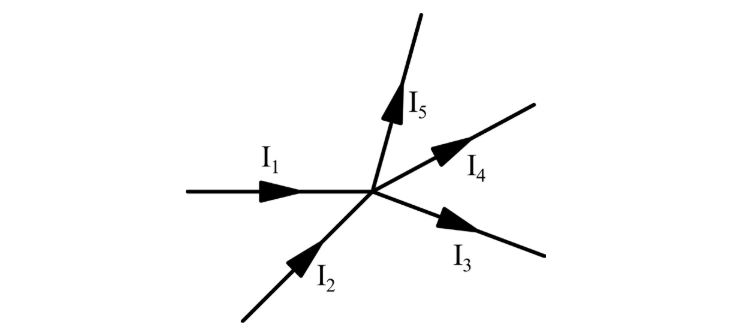
In above figure, the directions of the currents are known.
Kirchhoff’s first law states that: I1 + I2 = I3 + I4 + I5
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (2nd Law)
- It states that the algebraic sum of the voltages (or potential differences) around any closed loop in a circuit is equal to zero.
- This principle reflects the conservation of energy, meaning energy cannot be created or destroyed within the circuit.
- It is also known as Kirchhoff's Second Law or the Loop Rule.
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law Formula
Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
ΣV = 0
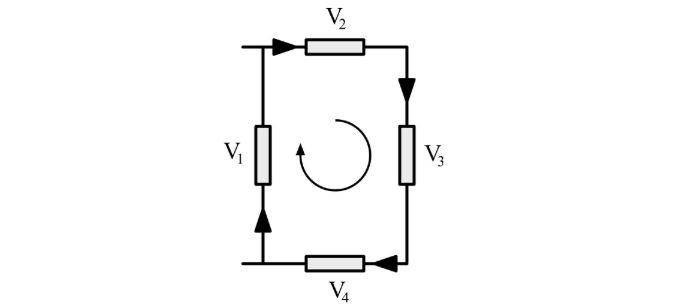
For above diagram, Kirchhoff’s second law states that: V1 + V2 + V3 + V4 = 0
In conclusion, Kirchhoff's Laws are fundamental principles that form the backbone of electrical circuit analysis and design.
Solved Examples of Kirchhoff's Law
Question. Determine the current in each branch of the network shown in the following figure.
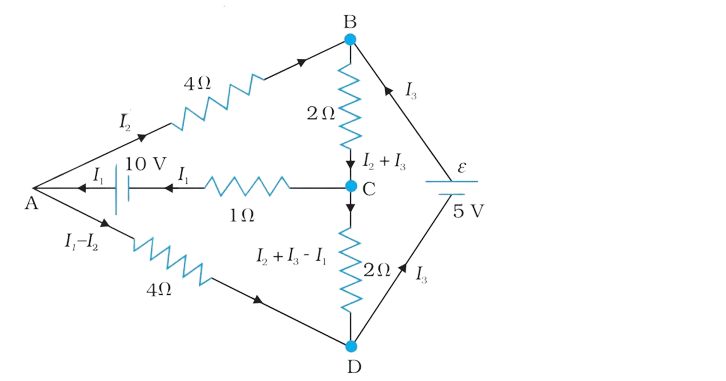
Solution:
Kirchhoff’s second rule for the closed loop ADCA gives,
10 – 4(I1 – I2 ) + 2(I2 + I3 – I1 ) – I1 = 0 …………..(i)
7I1 – 6I2 – 2I3 = 10
For the closed loop ABCA, we get
10 – 4I2 – 2(I2 + I3) – I1 = 0
I1 + 6I2 + 2I3 =10 ………………..(ii)
For the closed loop BCDEB, we get
5 – 2(I2 + I3 ) – 2(I2 + I3 – I1 ) = 0
2I1 – 4I2 – 4I3 = –5 …………………..(iii)
Solving equations (i), (ii) and (iii), we get:
I1 = 2.5A, I2 = 5/8 A, I3 = 15/8 A
The currents in the various branches of the network are
AB : 5/8 A, CA : 5/2 A, DEB : 15/8 A
AD : 15/8 A, CD : 0 A, BC : 5/2 A
Video Courses for PCMB
You can now access video lectures designed by experts for major topics of Physics, Chemistry, Maths and Biology to get a better concept clarity and achieve success in your academics. Find the video link below:
Also Check:

Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation