AFCAT vs CDS: Wondering how to join the Indian Armed Forces after graduation? AFCAT and CDS are the most common paths. Both exams open the doors to a prestigious uniform, a stable government job and an honourable life, but the career path, training, lifestyle and future opportunities are completely different. The key similarity is that both are conducted twice a year, and the SSB interview plays a crucial role in both exams. Lakhs of aspirants appear for these defence exams every year without actually knowing which exam truly matches their personality, long-term goals and strengths. Let’s compare both exams to help candidates identify the roles that suit them best.
What Is AFCAT?
The Indian Air Force conducts the Air Force Common Admission Test (AFCAT). It invites applications from Indian candidates to fill vacancies for Group ‘A’ Gazetted Officers in Flying and Ground Duty (Technical and Non-Technical) branches. Nearly 1.5 to 2 lakh applicants apply for the AFCAT exam every year.
What Is CDS?
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) organises the Combined Defence Services Examination (CDS). It is conducted for admission to IMA Dehradun, INA Ezhimala, AFA Hyderabad, and OTA Chennai. Around 2.5 lakh candidates apply for the CDS exam. CDS often attracts more applicants than AFCAT because it offers a variety of courses across three services. Even CDS releases a higher number of vacancies compared to AFCAT. This makes CDS a tougher and more competitive exam.
AFCAT vs CDS: Key Differences at a Glance
AFCAT and CDS are the toughest defence exams in the country.
AFCAT vs. CDS: Eligibility
The eligibility criteria differ for AFCAT and CDS. It depends on the post or course type of both exams.
| Partculars | AFCAT Eligibility | CDS Eligibility |
| Nationality | Citizen of India | (i) a Citizen of India, or (ii) a subject of Nepal, or (iii) a person of Indian origin who has migrated from Pakistan, Burma, Sri Lanka and East African Countries of Kenya, Uganda, the United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Malawi, Zaire and Ethiopia or Vietnam with the intention of permanently settling in India. |
| Age | Flying Branch through AFCAT and NCC Special Entry: 20 to 24 years Ground Duty (Technical & Non-Technical) Branch: 20 to 26 years | IMA: 19 years to 24 years INA: 19 years to 24 years AFA: 20 years to 24 years OTA: 19 years to 25 years |
| Educational Qualification | 12th pass and Graduation with minimum required marks. | IMA/OTA/AFA: Degree from a recognised University Indian Naval Academy: Degree in Engineering from a recognised University. |
CDS offers more opportunities compared to AFCAT. CDS focuses on a variety of courses, while AFCAT is known only for flying and ground duty branches.
AFCAT vs. CDS: Selection Process
The AFCAT and CDS differ in the selection process. AFCAT selection includes stages, i.e. written exam and the AFSB interview. AFSB Testing covers the Officer Intelligence Rating Test and Psychological Test. The written test evaluates candidates on areas like General Awareness, Verbal Ability, Numerical Ability, Reasoning and Military Aptitude Test.
The CDS selection process involves stages: a written exam and an SSB interview round. The written test aims to evaluate the candidate’s understanding of English, GK, and Mathematics. CDS is more difficult than AFCAT because it offers admission to numerous academies.
AFCAT vs. CDS: Salary
The salary of an AFCAT and a CDS officer is the same. Upon clearing the selection process, the cadets will receive a fixed stipend of Rs 56100 per month during the training period. On successful commissioning, the pay matrix of the Officer commissioned shall be fixed in Level 10 (Rs. 56100- 177500). The Military Service Pay (MSP) to the officers is fixed at INR 15,500 per month. They will also enjoy various allowances based on their nature of duty and job location.
AFCAT vs. CDS: Job Profile
The job profiles of AFCAT and CDS are completely different. AFCAT is perfect for those who prefer aircraft and modern technology. CDS is suitable for those who wish to move to leadership roles. The AFCAT Job Profile for different posts are:
-
Flying Branch: Handle and take care of fighter jets.
-
Ground Duty (Technical): Ensure proper maintenance of aircraft tools and technical equipment.
-
Ground Duty (Non-Technical): Handle tasks related to administration, logistics, and accounts.
Career Path After AFCAT vs CDS
The career growth in AFCAT and CDS is quite attractive. The promotions are granted based on your seniority, job performance, and internal exams. But promotions in the AFCAT are faster than CDS in the initial years. But CDS offers long-term growth and higher positions. The promotion hierarchy for both career paths is:
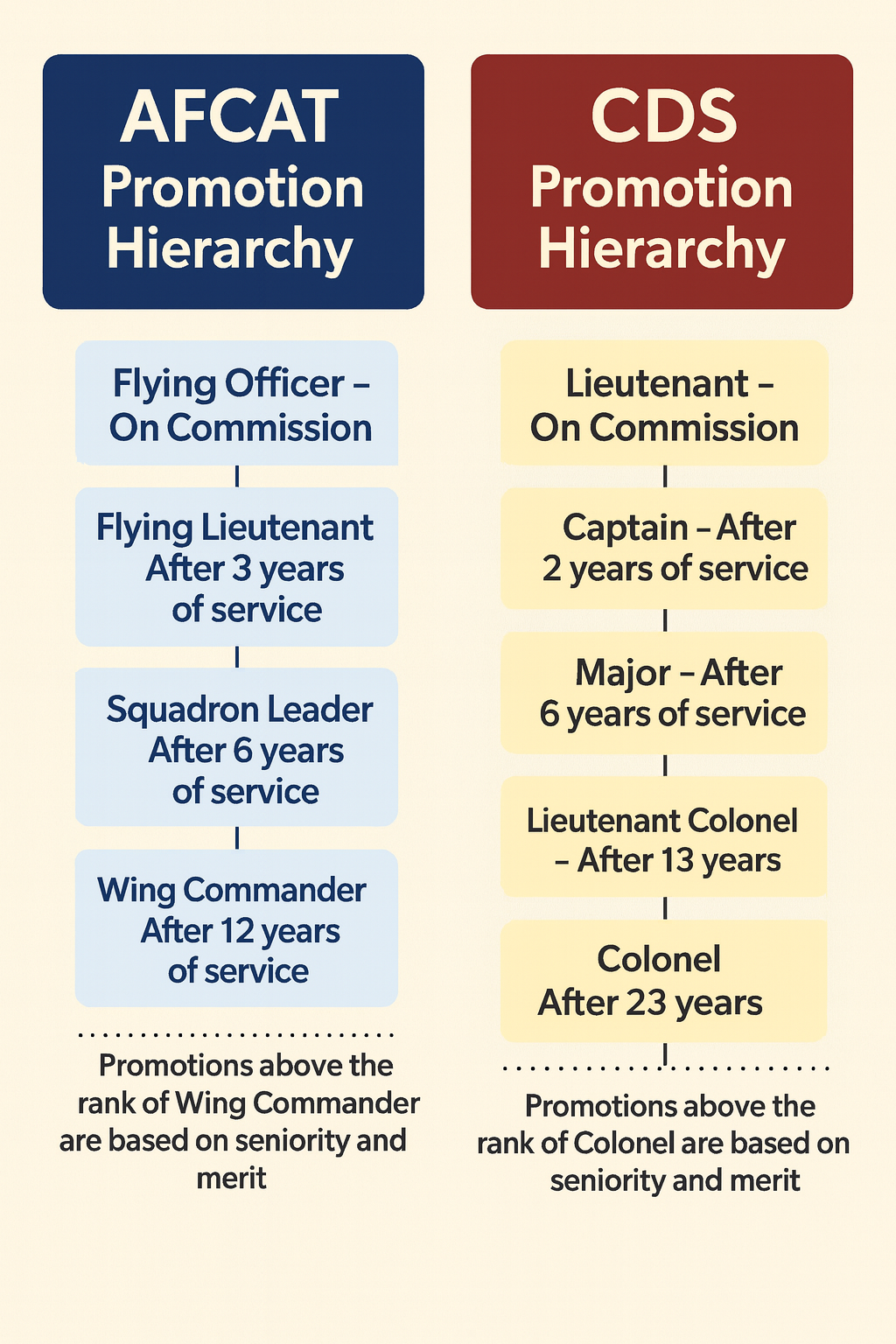
AFCAT vs. CDS: Which One Should You Choose?
Choose the AFCAT if you enjoy technology and flying. Choose the CDS if you want to explore leadership roles. AFCAT offers faster growth and a balanced lifestyle compared to CDS roles.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation