Fundamental Rights of India: Do you know that the section on Fundamental Rights is often referred to as the ‘conscience’ of the Indian Constitution? During the struggle for freedom, the leaders had realized the importance of rights. When India became independent, there were no doubts on the protection of rights in the Constitution. The rights that would be specially protected were named ‘fundamental rights’. In this article, we have provided explanations for the six fundamental rights guaranteed to the citizens by the Constitution.
What are fundamental rights?
The Constitution of India lists the rights that are specially protected as fundamental rights. They are called fundamental as these rights are so essential that there are special provisions in the Constitution for their protection. These rights are necessary for the sustenance of our democratic nation. Articles 12-35 in Part III of the Constitution deals with these inviolable rights.
What is the importance of fundamental rights?
As the name suggests, fundamental rights are fundamental to our life. Underlining the importance of these rights, NCERT, explains, ‘’In a democracy every citizen has to have the right to vote and the right to be elected to government. For democratic elections to take place, it is necessary that citizens should have the right to express their opinion, form political parties and take part in political activities. Rights protect minorities from the oppression of the majority. Rights are guarantees which can be used when things go wrong. Sometimes elected governments may not protect or may even attack the rights of their own citizens. That is why some rights need to be placed higher than the government, so that the government cannot violate them.’’
How are fundamental rights different from other rights?
Fundamental rights are guaranteed by the Constitution, while other rights are protected by ordinary law. Other rights can be changed by normal process of law, while fundamental rights can be changed by amending the Constitution. No organ of the government can violate fundamental rights.
What are the fundamental rights given in the Constitution?
The six fundamental rights guaranteed in the Constitution of India are-
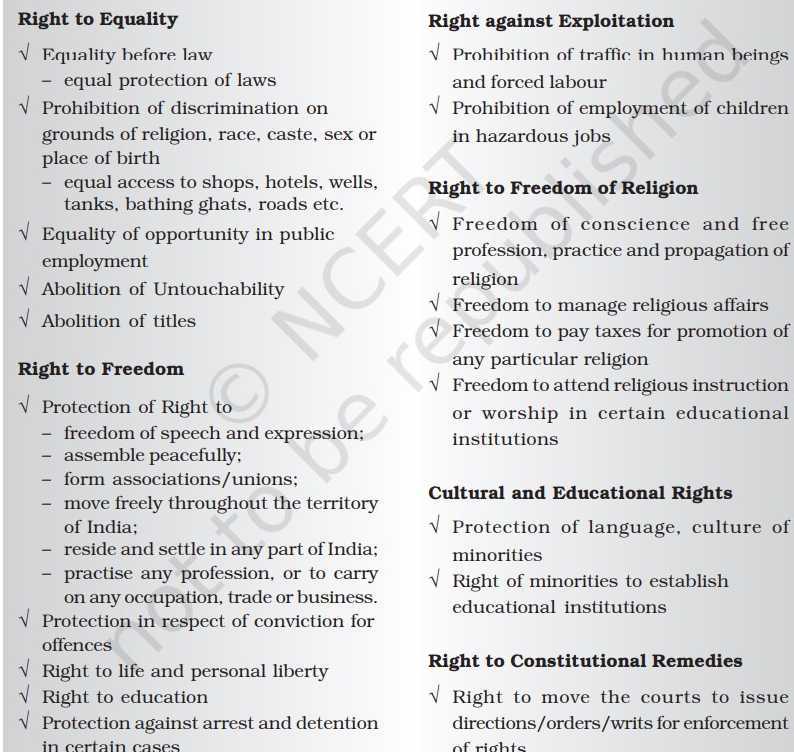
Right to Equality (Articles 14-18)
Right to Freedom (Articles 19-22)
Right against Exploitation (Articles 23-24)
Right to Freedom of Religion (Articles 25-28)
Right to Constitutional Remedies (Article 32)
Cultural and Educational Rights (Articles 29-30)
Right to Equality
According to the Constitution, every citizen of the country is equal before the law. The laws are applicable to all in the same manner without any discrimination. The state shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth. Every citizen shall have access to public places like shops, restaurants, hotels, cinema halls, wells, tanks, bathing ghats, roads and playgrounds. All citizens shall have equality of opportunity in matters relating to employment. The Constitutions forbids the practice of untouchability in any form. The state shall not confer titles on anybody whether a citizen or a non-citizen.
Also Read: Democratic Rights Class 9 Notes: CBSE 9th Social Science Chapter 5, Download PDF Here
Right to Freedom
The right to freedom includes:
Freedom of speech and expression- Citizens have the right to freely communicate their views and opinions.
Assembly in a peaceful manner- Citizens have the freedom to hold meetings and rallies.
Form associations and unions- Citizens have the freedom to form associations and unions.
Move freely throughout the country- Citizens have the right to travel to any part of the country without restriction.
Reside in any part of the country- Citizens have the freedom to live anywhere in the country.
Practice any profession, or to carry on any occupation, trade or business- Citizens have the right to choose and practice a profession or business of their choice.
The Constitution says that no person can be deprived of his life or personal liberty except according to procedure established by law.
Right against Exploitation
The Constitution prohibits traffic in human beings. It also prohibits forced labour in any form. Employing children below the age of 14 years in any hazardous profession is prohibited.
Right to Freedom of Religion
India is a secular state which means that there is no official religion. Every citizen has the freedom to practice a religion of their choice. Citizens have the freedom to profess, practice and propagate the religion they choose. Every religious group is free to manage its religious affairs. No one has the right to force another person to convert into their religion. There shall be no religious instruction in government educational institutions. In private educational institutions no person shall be compelled to take part in any religious instruction.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
According to NCERT, ‘’The right to constitutional remedies is considered the ‘heart and soul of the constitution’. It is so because this right gives a citizen the right to approach a High Court or the Supreme Court to get any of the fundamental rights restored in case of their violation. The Supreme Court and the High Courts can issue orders and give directives to the government for the enforcement of rights.’’
Cultural and Educational Rights
The cultural and educational rights give citizens the right to- any section of citizens with a distinct language or culture have a right to conserve it, admission to any educational institution maintained by government or receiving government aid cannot be denied to any citizen on the ground of religion or language, minorities have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
CBSE Video Courses for All Subjects for Class 10 Students
Class 10 students can study effectively with the help of video courses prepared by the subject matter experts. These video courses will explain the concepts in a simple and interactive manner which will help learners to understand clearly. The videos are available for all major subjects which includes social studies. Refer to the below link: 
Note: All images have been taken from NCERT Class 11 Political Science textbook (Indian Constitution at Work).
Also, check
Judiciary: Definition, Role, Importance, Structure And More
Autocratic: Meaning, Features, Advantages And Disadvantages of Autocracy And More
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation