ICSE Class 10 Biology Practice Paper 2023: The Class 10th ICSE board Biology paper is going to be held on 29 March 2023. This is the right time to take a look at important practice questions and increase your chances of scoring good marks in the exam. ICSE Class 10 Biology is Paper 3 of the Science course (Code: 52). It’s comparatively easier than Chemistry and Physics, but due to the advanced syllabus of the CISCE board, Biology is much tougher than it appears. Students should take it seriously and study with dedication. An effective way to succeed in biology is by practising important questions before the exam. We have prepared an ICSE Class 10 Biology practice paper consisting of crucial questions for last minute revision before the exam. You can read and download the ICSE Class 10 Biology practice paper 2023 here.
Related:
ICSE 10th Biology Practice Questions 2023
MCQs
1. ___is the U-shaped portion of a nephron.
a) PCT
b) DCT
c) Loop of Henle
d) Collecting duct.
Ans: c) Loop of Henle
2. The process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets from leaf margins.
a) Guttation
b) Transpiration
c) Bleeding
d) Evaporation
Ans: a) Guttation
3. Movement of molecules of a substance from their higher concentration to lower concentration when they are in direct contact.
a) Diffusion
b) Endosmosis
c) Imbibition
d) Active transport
Ans: a) Diffusion
4. The chromatin material is formed of
a) DNA only
b) DNA and Histones
c) Histones only
d) Nucleotides
Ans: b) DNA and Histones
5. The state of a cell when the cell wall is rigid and stretched by the increase in volume due to the absorption is called
a) Flaccidity
b) Turgidity
c) Capillarity
d) Tonicity
Ans: b) Turgidity
6. Ureter is the connecting link between kidney and
a) Urethra
b) Urinary bladder
c) Sphincter
d) Collecting duct.
Ans: b) Urinary bladder
7. A blood vessel which has small lumen and thick wall is
a) Capillary
b) Artery
c) Vein
d) Venule
Ans: b) Artery
8. A plant is which leaves have thick cuticle is
a) Rose
b) Neem
c) Papaya
d) Banyan
Ans: d) Banyan
9. Pulse wave is mainly caused by
a) Systole of atria
b) Diastole of atria
c) Systole of the left ventricle
d) Systole of right ventricle
Ans: c) Systole of the left ventricle
10. Smallest WBCs are-
a) Lymphocytes
b) Monocytes
c) Basophils
d) Neutrophils
Ans:a) Lymphocytes
Short Answer and Long Answer Questions:
11. A healthy croton plant bearing variegated leaves was kept in a dark cupboard to destarch it, after which it was placed in sunlight for a few hours. One of the leaves was then plucked and an outline of the leaf marking the green and the nongreen regions was drawn. The leaf was then tested for starch.
Using the above information, answer the following question.
i) State the aim of the experiment.
Ans: To detect the presence of starch in plant leaf.
ii) Name the chemical used for testing the presence of starch.
Ans: Iodine
iii) Why is the leaf boiled in water and alcohol before testing for the presence of starch?
Ans: To extract chlorophyll and eliminate the green color from the leaf.
iv) What change is seen in the leaf after the starch test.
Ans: Nongreen regions show no change of color. Green areas turned brown to blue-black.
v) Give two examples of variegated leaves.
Ans: coleus and Euonymus microphylla
12. With reference to the ‘Human eye’ answer the given question.
i) Name the part of retina on which an object is focused for the clearest vision.
Ans: Fovea
ii) Which structure in the eye is mainly responsible for
a) Change in the size of the pupil. Iris muscles
b) Transmission of impulses from the eye to the brain. Optic nerves
c) Alteration of the shape of the lens. Ciliary muscles
d) Converting the light rays into electrical impulse. Retina
ii) What is meant by ‘Power of Accommodation of the Eye’?
Ans: It is the ability of the eye lens to focus the light directly onto the retina by changing its focal length. It ensures the formation of clear and sharp image.
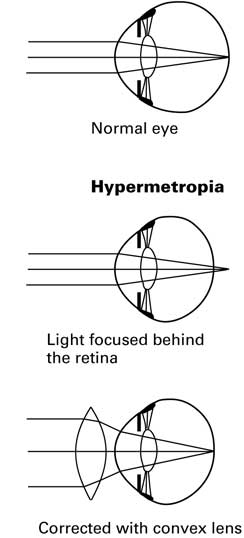
iv) How can long-sightedness be corrected? Explain briefly with the help of a diagram.
Ans: Long-sightedness is also called hypermetropia or hyperopia. In this condition, the light is focused behind the retina. It can be corrected by wearing glasses with convex lenses.
13. State the exact location of the following.
a) Cochlea: in the temporal bone of the inner ear.
b) Arachnoid layer: directly below the dura mater in the skull region.
c) Mitral valve: between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
d) Adrenal glands: Superior/ top of each Kidney.
e) Corpus callosum: in the center of the brain at the base of the longitudinal fissure.
14. Give one point of difference between the following on the basis of what is indicated in the brackets.
i) Corpus callosum and corpus luteum (function)
Corpus callosum: Connect left and right cerebral hemispheres
Corpus luteum: secretion of progesterone hormone.
ii) Thyroid gland and Adrenal gland (secretions they produce)
Thyroid gland: Secretion of T3 and T4 thyroid hormones
Adrenal gland: Secretes adrenaline
iii) Mitosis and meiosis (number of daughter cells produced)
Mitosis: 2 daughter cells
Meiosis: 4 daughter cells
iv) Micturition and Parturition (Definition)
Micturition: Excretion of urine out of the body
Parturition: Delivery of baby out of the body
v) Sensory nerve and motor nerve (direction of impulse carried)
Sensory nerve: Take impulses towards the central nervous system.
Motor nerve: Carry impulses from central nervous system to the muscles or site of action.
15. A homozygous tall plant (T) bearing red coloured (R) flowers is crossed with a homozygous dwarf (t) plant bearing white (r) flowers.
i) give the genotype and phenotype of the plants of F1 generation.
Ans: Genotype: TtRr, Phenotype: Tall and Red flowers
ii) State the possible combinations of the gametes that can be obtained from the F1 hybrid plant.
Ans: Possible combinations for F2 generation when F1 hybrids cross.
| ♂️\♀️ | TR | Tr | tR | tr |
| TR | TTBB | TTRr | TtRR | TtRr |
| Tr | TTRr | TTrr | TtRr | Ttrr |
| tR | TtRR | TtRr | ttRR | ttRr |
| tr | TtRr | Ttrr | ttRr | ttrr |
iii) Explain Mendel’s law of dominance
Ans: According to the Mendel’s law of dominance, in an allele pair containing one dominant and one recessive allele, only the dominant allele will express.
iv) Mention the phenotypes of the offsprings obtained in F2 generation.
Ans: F2 combinations:
- Tall and Red
- Tall and White
- Dwarf and Red
- Dwarf and White
v) What are the two application of mendel’s laws?
- Ans: The laws help in predicting the genotype and phenotype of the progeny if parent genotypes are known.
- We can determine the unknown genotype of an organism.
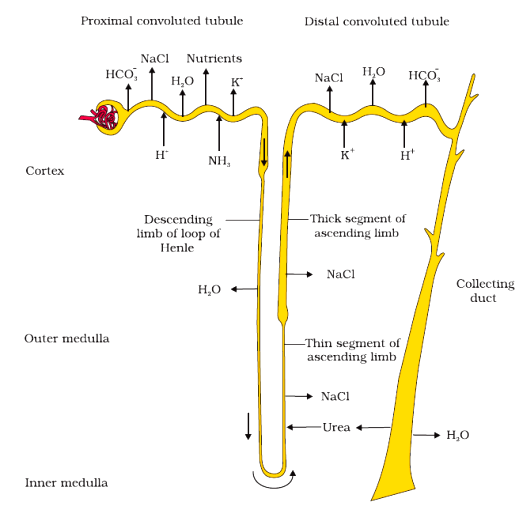
vi) Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of a single Renal tubule.
16. Given below are sets of five terms each. In each case, rewrite the terms in logical sequence.
a) Implantation, Parturition, ovulation , Gestation, Fertilization.
Ans: Ovulation, Fertilization, Implantation, Gestation, Parturition
b) Conjunctiva, Retina, Cornea, optic nerve, Lens.
Ans: Conjuctiva, Cornea, Lens, Retina, Optic Nerve
c) Vena cava, Intestinal artery, Hepatic vein, Hepatic portal vein.
Ans: Intestinal artery, hepatic portal vein, hepatic vein, vena cava
d) Photolysis, polymerization, Activation of chlorophyll, photophosphorylation, NADP to NADPH.
Ans: Photolysis, activation of chlorophyll, photophosphorylation, NADP to NADPH, Polymerization
e) Xylem vessels, mesophyll cells, stoma, Intercellular space, substomatal space.
Ans: Xylem vessels, substomatal space, Intercellular space, mesophyll cells, stoma
17. State the main function of the following.
a) Alpha cells of Pancreas: Secrete glucagon
b) Prostate gland: Secrete prostatic fluid to form semen.
c) Phloem: Carry carbohydrates and nutrients from leaves to other parts of the plant.
d) Pulmonary artery: Carry blood from the right ventricle to pulmonary circulation.
e) Choroid layer of eye: bring oxygen and nutrients to the eye.
18. Expand the following abbreviation
i) NADP: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
ii) ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone
iii) ODF: Osteoclast Differentiation Factor
iv) GMO: Genetically modified organisms
v) PNS: Peripheral nervous system
Check other Important resources for ICSE Class 10th Exams 2023.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation