NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7: Students should have access to correct solutions to the exercise questions so as to determine if their approach is right or not. This becomes crucial when solving numerical problems in a subject like Physics. It is not unheard of that students get scared of solving such questions. But with the right amount of practice, they can score well in the 2025 exams. This article will help CBSE Class 12 Science students. We have given NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current here.
At Jagran Josh, these solutions are prepared by the subject experts for the benefit of students. The exercise questions given in the NCERT books help students to analyse their understanding of the concepts involved in a chapter but also in preparing for the examinations. Students should solve as many questions as they can to strengthen their understanding and ability to answer questions.
Also Check:
| CBSE Class 12 Physics Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme for 2025 |
Students can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current from the direct link given in this article. The solutions have been given in PDF format so students can save and view the PDFs on phones, tablets, computers and laptops.
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current Solutions
Students go through the questions from NCERT Class 12 Chapter 7 Alternating Current carefully.
EXERCISES
7.1. A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply.
(a) What is the rms value of current in the circuit?
(b) What is the net power consumed over a full cycle?
Sol. Given,
R = 100 ohms
V = 220 V
f = 50 Hz
(a) Irms = Vrms / R
Substituting,
Irms = 220 / 100 = 2.2 A
(b) Power = V.I
Or Power = 220 x 2.2
Or Power = 484 W
7.2. (a) The peak voltage of an ac supply is 300 V. What is the rms voltage?
(b) The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current?
Sol. (a) Vrms = Vpeak / 1.414
Vrms = 300 / 1.414
Or Vrms = 212.13 V
(b) Using above identity for current
Ipeak = 1.414 x Irms
Or Ipeak = 1.414 x 10 = 14.14 A
7.3. A 44 mH inductor is connected to 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
Sol. Given,
L = 44 mH
V = 220 V
f = 50 Hz
Irms is given by= V / XL
Determining inductive reactance
XL= 2 x 3.14 x 50 x 44 x 10-³
XL= 13.82 ohms
Therefore,
Irms=220 / 13.82
Or Irms=15.92 A
7.4. A 60 μF capacitor is connected to a 110 V, 60 Hz ac supply. Determine the rms value of the current in the circuit.
Sol. Given,
C = 60 microfarads
V = 110 volts
f = 60 hertzs
Irms = V / Xc
Now
Xc = 1 / (2 x 3.14 x 60 x 60 x 10-⁶)
Xc = 44.248 ohms
Hence
Irms = 110 / 44.248 = 2.488 A
7.5. In Exercises 7.3 and 7.4, what is the net power absorbed by each circuit over a complete cycle. Explain your answer.
Sol. (a) In the case of the inductive network,
The RMS current value is I = 15.92 A
The RMS voltage value is V = 220 V
Therefore, the total power taken can be derived by the following equation: P = VI cos Φ
In the case of a purely inductive circuit, the difference in the phase of an alternating voltage and an alternating current is 90°, i.e. Φ = 90°.
Therefore, P = 0
Thus, the total power absorbed by the circuit is zero.
(b) In the case of the capacitive network, we know that The value of RMS current is given by, I = 2.49 A
The value of RMS voltage is given by, V = 110 V
Thus, the total power absorbed can be derived from the following equation: P = VI Cos Φ
The phase difference between alternating voltage and alternating current is 90° i.e. Φ = 90°. Thus , P = 0
Therefore, the net power absorbed by the circuit is zero.
7.6. A charged 30 μF capacitor is connected to a 27 mH inductor. What is the angular frequency of free oscillations of the circuit?
Sol. Given,
C = 30 microF
L = 27 mH
Angular frequency of free oscillations = 1/√LC
Substitution results
Angular frequency = 1111.11 /s
7.7. A series LCR circuit with R = 20 Ω, L = 1.5 H and C = 35 μF is connected to a variable-frequency 200 V ac supply. When the frequency of the supply equals the natural frequency of the circuit, what is the average power transferred to the circuit in one complete cycle?
Sol. Given,
R = 20 ohms
L = 1.5 henries
C = 35 microfarad
V = 200 volts
Natural frequency
=1/√LC
= 138 /s
At natural frequency,
Z = R
So I = V / R = 200 / 20 = 10 A
Thus
P = I²R
Or P = 10 x 10 x 20 = 2000 W
7.8. Figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency 230 V source. L = 5.0 H, C = 80 μF, R = 40 Ω.
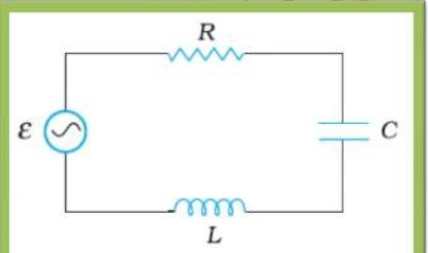
(a) Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.
(b) Obtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.
(c) Determine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.
Sol. Given,
V = 230 V
L = 5 H
C = 80 μF
R = 40 ohms
(a) Source frequency at resonance=1/√LC
Solving by putting respective values
= 50 rad / s
(b) At resonance,
Impedance, Z = Resistance, R
So Z = R = 40 ohms
Now rms value of current,
I = V / R
Or I = 230 / 40
Hence I = 5.75 A
Amplitude of this value of current = 1.414 x I
= 1.414 x 5.75
= 8.13 A
(c ) Now taking into consideration the rms potential drops
Across Resistance
VR= IR
= 5.75 x 40
= 230 V
Across Capacitance
VC= IXC
= 1437.5 V
Across Inductance
VL= IXL
=5.75 x 50 x 5
=1437.5 V
Across LC combination
VLC= I(XL–XC)
= 0(at resonating frequency)
To download these solutions in pdf, refer to the below link:
| Download NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 7 Alternating Current Solutions PDF |
Also, check
- CBSE 12th Date Sheet 2025 Download PDF
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Study Material for 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Most Repeated Questions
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Competency-Based Questions With Answer Key 2024-25
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Topper Answer Sheet for 2025 Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics 90 Days Study Plan for 2025 Exam
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 (2024-2025) All Subjects
- NCERT Books for CBSE Class 12 - Latest Edition
- NCERT Rationalised Content for Class 12
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation