Term 2 CBSE Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2022 is available here for download in PDF format. The link to download the PDF is given at the end of this article. Students preparing for Term 2 CBSE Class 11 Annual Exams should plan their studies accordingly.
NCERT Books for Class 11 (PDF): All Subjects
Term 2 CBSE Class 11 Physics Syllabus 2021-22
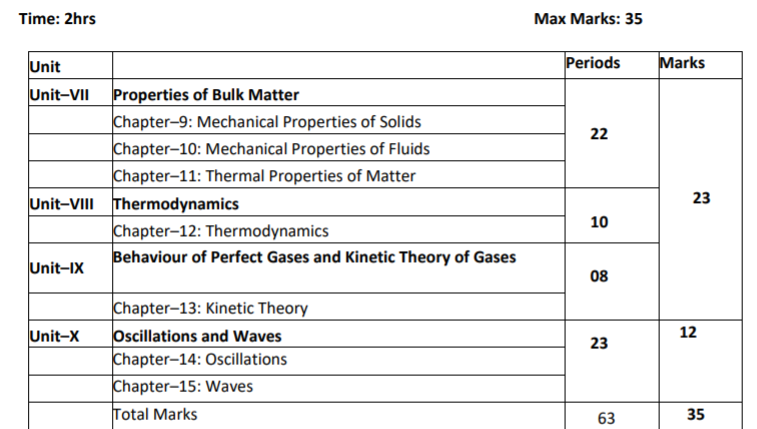
Unit VII: Properties of Bulk Matter
Chapter–9: Mechanical Properties of Solids
Stress-strain relationship, Hooke's law, Young's modulus, bulk modulus
Chapter–10: Mechanical Properties of Fluids Pressure due to a fluid column; Pascal's law and its applications (hydraulic lift and hydraulic brakes), effect of gravity on fluid pressure. Viscosity, Stokes' law, terminal velocity, streamline and turbulent flow, critical velocity, Bernoulli's theorem and its applications. Surface energy and surface tension, angle of contact, excess of pressure across a curved surface, application of surface tension ideas to drops, bubbles and capillary rise.
Chapter–11: Thermal Properties of Matter Heat, temperature, (recapitulation only) thermal expansion; thermal expansion of solids, liquids and gases, anomalous expansion of water; specific heat capacity; Cp, Cv - calorimetry; change of state - latent heat capacity. Heat transfer-conduction, convection and radiation (recapitulation only), thermal conductivity, qualitative ideas of Blackbody radiation, Wein's displacement Law, Stefan's law, Greenhouse effect.
Unit VIII: Thermodynamics
Chapter–12: Thermodynamics Thermal equilibrium and definition of temperature (zeroth law of thermodynamics), heat, work and internal energy. First law of thermodynamics, isothermal and adiabatic processes. Second law of thermodynamics: reversible and irreversible processes Unit IX: Behaviour of Perfect Gases and Kinetic Theory of Gases
Chapter–13: Kinetic Theory
Equation of state of a perfect gas, work done in compressing a gas. Kinetic theory of gases - assumptions, concept of pressure. Kinetic interpretation of temperature; rms speed of gas molecules; degrees of freedom; law of equi-partition of energy (statement only) and application to specific heat capacities of gases; concept of mean free path, Avogadro's number.
Unit X: Oscillations and Waves
Chapter–14: Oscillations Periodic motion - time period, frequency, displacement as a function of time, periodic functions. Simple harmonic motion (S.H.M) and its equation; phase; oscillations of a loaded spring- restoring force and force constant; energy in S.H.M. Kinetic and potential energies; simple pendulum derivation of expression for its time period. Free, forced and damped oscillations (qualitative ideas only), resonance.
Chapter–15: Waves Wave motion: Transverse and longitudinal waves, speed of travelling wave, displacement relation for a progressive wave, principle of superposition of waves, reflection of waves, standing waves in strings and organ pipes, Beats
The record, to be submitted by the students, at the time of their annual examination, has to include:
Record of at least 4 Experiments, to be performed by the students
Record of at least 3 Activities [with 3 each from section A and section B], to be demonstrated by the teacher.
Time Allowed: One and half hours Max. Marks: 30
Two experiments one from each section: 8 Marks
Practical record (experiment and activities): 2 Marks
Viva on experiments, and activities: 5 Marks
Total: 15 Marks
Experiments
1. To determine Young's modulus of elasticity of the material of a given wire.
OR
To find the force constant of a helical spring by plotting a graph between load and extension.
2. To study the variation in volume with pressure for a sample of air at constant temperature by plotting graphs between P and V, and between P and 1/V.
3. To determine the surface tension of water by capillary rise method. To determine the coefficient of viscosity of a given viscous liquid by measuring terminal velocity of a given spherical body.
4. To study the relationship between the temperature of a hot body and time by plotting
a cooling curve.
5. To determine specific heat capacity of a given solid by method of mixtures.
6. To study the relation between frequency and length of a given wire under constant tension using a sonometer.
OR
To study the relation between the length of a given wire and tension for constant frequency using a sonometer.
7. To find the speed of sound in air at room temperature using a resonance tube by two resonance positions.
Activities
1. To observe change of state and plot a cooling curve for molten wax.
2. To observe and explain the effect of heating on a bi-metallic strip.
3. To note the change in level of liquid in a container on heating and interpret the observations.
4. To study the effect of detergent on surface tension of water by observing capillary rise.
5. To study the factors affecting the rate of loss of heat of a liquid.
6. To study the effect of load on depression of a suitably clamped metre scale loaded at
(i) its end (ii) in the middle.
7. To observe the decrease in pressure with increase in velocity of a fluid.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation