Iron makes up about 5 per cent of the Earth's crust and is the most abundant element in the whole Earth (about 35 per cent). It is the second most abundant metal after aluminium and the fourth most abundant overall after oxygen, silicon, and aluminium by weight.
The Earth's core is primarily iron and nickel. The outer core is liquid, while the inner core is solid. Heat from the inner core and Earth's rotation cause the liquid iron in the outer core to swirl and convect.
This movement of conductive iron generates electrical currents, which in turn produce the magnetic field. This abundance of iron (and a smaller amount of nickel) in the core is crucial for Earth's magnetic shield.
Iron in the human body is found to be about 4.5 grams, of which approximately 65 per cent is in the form of haemoglobin, which transports molecular oxygen from the lungs throughout the body.
Speaking of availability, iron is found on Earth primarily as iron ore (iron oxides like haematite) in solid rock formations. Most commercially mined iron comes as iron ore. Key Indian states with iron ore deposits include Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
Extracting useable iron from iron ores requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching 1,500 degrees Celsius. It was during the 2nd millennium BC that humans started to use iron tools and weapons. That marked the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age (1200 BCE).
In today's modern world, iron alloys like stainless steel, steel, cast iron, etc., are most commonly used.
Let us now understand the chemical name and formula of iron along with its properties.
What is the chemical name and formula of Iron?
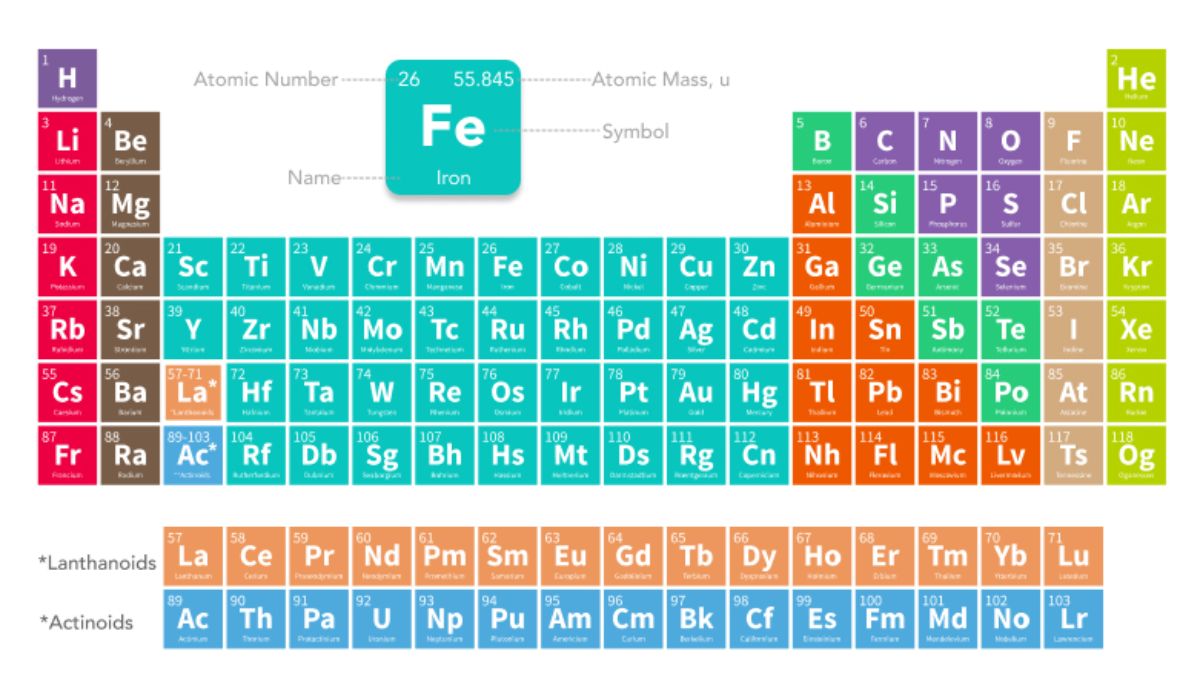
The chemical name of iron is simply iron. The chemical formula and symbol of iron is Fe, which comes the Latin word Ferrum.
Iron is chemically referred to Fe in the periodic table. It is an ferrous element with atomic number 26.
Iron is a solid at 25°C (room temperature).
Properties of Iron

| Property | Value |
| Atomic Number | 26 |
| Atomic Mass | 55.845 atomic mass units (u) |
| Density | 7.87 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 1,538 degrees Celsius |
| Boiling Point | 2,862 degrees Celsius |
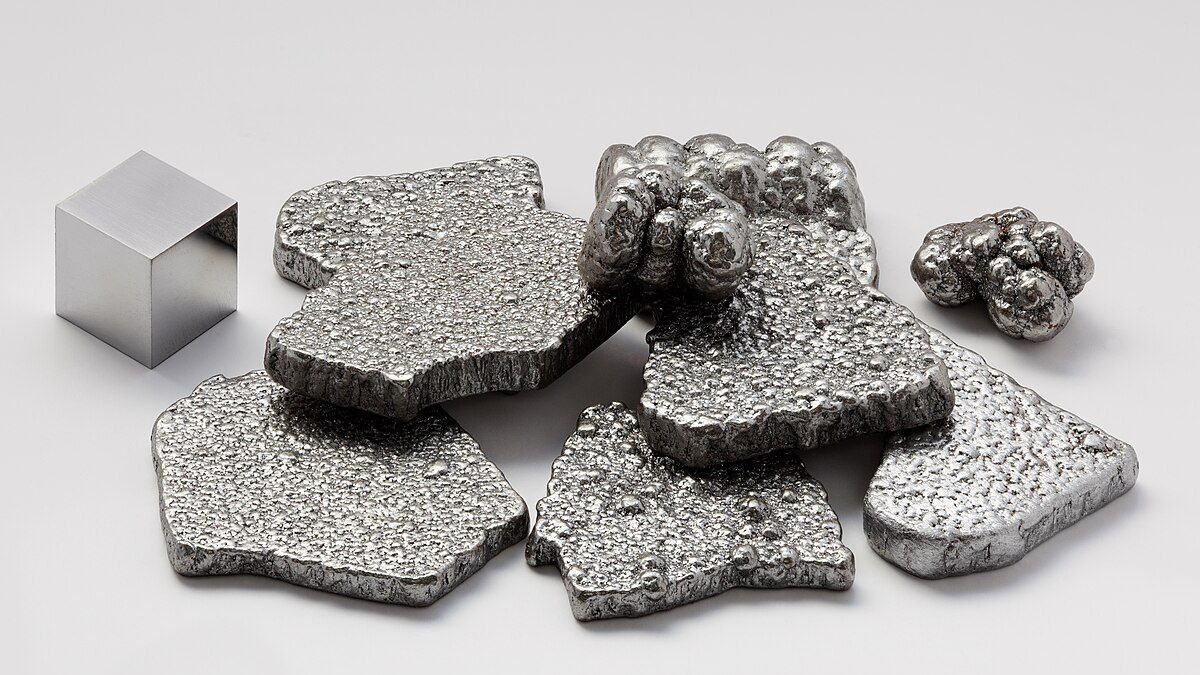
Iron (Fe) is a ferromagnetic metal with high tensile strength. It is shiny and silver-grey in colour.
Iron is a good conductor of heat and electricity, but less than copper.
Iron is both malleable (can be hammered or rolled into sheets under compression) and ductile (can be stretched or drawn into wires under tension).
Common Uses of Iron
Iron is mainly used in:
- Steel industry and construction (buildings, vehicles, ships, bridges, etc)
- Cast iron items and pipes
- Catalysts in chemical processes
- Machinery and Tools
- Appliances and utensils
- Making magnets
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation