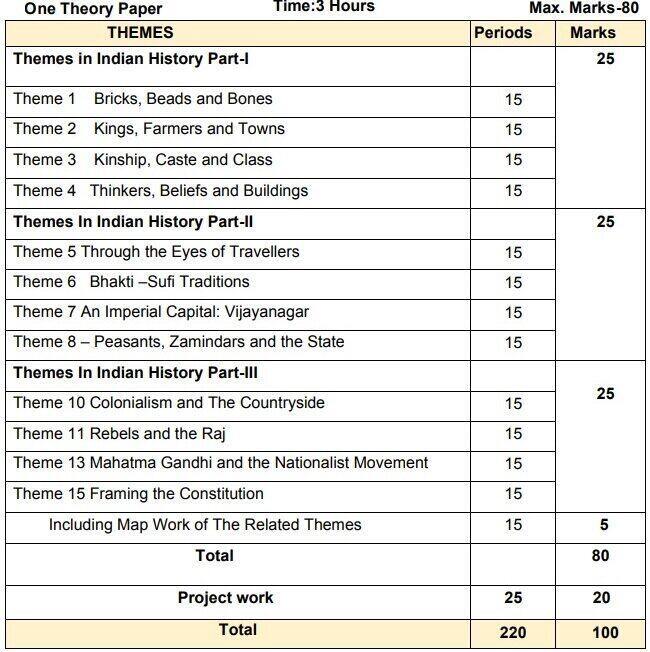
CBSE Class 12 History Syllabus 2022-2023 is provided here for download in PDF. The History syllabus for class 12 is divided into various themes under which the topics are mentioned along with the learning objectives and outcomes. There are total 15 themes which are divided into 3 parts with each part carrying a weightage of 25 marks. The map work of the related themes is assigned a weightage of 5 marks. Students can check the details in the latest CBSE Class 12 History Syllabus to prepare for their board exams in the right manner. Check and download the syllabus below.
| Must Reads for CBSE Class 12 History Exam 2023 |
| CBSE Class 12 History Deleted Syllabus 2023 |
| CBSE Class 12 History Practice Paper 2023 |
| CBSE Class 12 History Topper Answer Sheet |
| Important MCQs| Important Case Study| Important Assertion Reason Questions |
CBSE Class 12 History (Code No. 055) Course Structure 2022-23
Also Check CBSE Class 12 Syllabus of All Subjects for 2022-2023 Session (PDF)
Class XII: Themes in Indian History
| Class XII: Themes in Indian History | ||
| Themes | NOTE- This is not an exhaustive list. For reflective teaching- learning process, explicit Learning Objectives and Outcomes can be added by teachers during the course-delivery for student’s real learning
| |
|
| Learning Objective | Learning Outcomes |
| Part-I BRICKS, BEADS AND BONES The Harappan Civilization: Broad overview: Early urb an centers Story of discovery: Harappan civilization Excerpt: Archaeological report on a major site Discussion: How it has been utilized by archaeologists/ historians | ● Familiarize the learner with early urban centers as economic and social institution. ● Introduce the ways in which new data can lead to a revision of existing notions of history. | At the completion of this unit students will be able to: ● State and deduce the multi-lateral aspects of Harappan civilization in order to understand the first civilization of the world. ● Develop an ability to use and analyze socio- economic, political aspects of Harappa ● Investigate and interpret historical and contemporary sources and viewpoints of ASI and historians on Harappa. |
| KINGS, FARMERS AND TOWNS:Early States and Economies (c. 600 BCE-600 CE) Broad overview: Political and economic History from the Mauryan to the Gupta period Story of discovery: Inscriptions and the Decipherment of the script. Shifts in the Understanding of political and economic history. Excerpt: Ashokan inscription and Gupta period land grant Discussion: Interpretation of inscriptions by historians. | ● Familiarize the learner with major trends in the political and economic history of the subcontinent. ● Introduce inscripti onal analysis and the ways in which these have shaped the understanding of political and economic processes. | At the completion of this unit students will be able to: ● Explain major trends in the 6th century BCE in order to understand the political and economic history of the subcontinent. • Analyze inscriptional evidences and the ways in which these have shaped the understanding of political and economic processes. |
| KINSHIP, CASTE AND CLASS Early Society Societies (C. 600 BCE-600 CE) Broad overview: Social Histories: Using the Mahabharata Issues in social history, inclu ding caste, class, kinship an d gender Story of discovery: Transmission and publications of the Mahabha rat Excerpt: from the Mahabharata, illustrating how it has been used by historians. Discussion: Other sources for reconstructing social history. | ● Familiarize the learners with issues in social history. ●Introduce the strategies of textual analysis and their use in reconstructing social history | At the completion of this unit students will be able to ● Analyze social norms in order to understand the perspectives of society given in the scriptures of ancient India. ●Examine the varied dimensions explored by historians in order to understand dynamic approach of Mahabharata. |
| THINKERS, BELIEFS AND BUILDINGS Cultural Developments (c. 600 BCE - 600 CE) Broad overview: A History of Buddhism: Sanchi Stupa a) A brief review of religious histories of Vedic religion, Jainism, Vaishnavism, Shaivism (Puranic Hinduism) b) b) Focus on Buddhism. Story of discovery: Sanchi stupa. Excerpt: Reproduction of sculptures from Sanchi. Discussion: Ways in which sculpture has been interpreted by historians, other sources for reconstructing the history of Buddhism. | ● Discuss the major religious developments in early India. ● Introduce strategies of visual analysis and their use in reconstructing the theories of religion. | At the completion of this unit students will be able to: ●Compare the distinct religious facets in order to understand the religious developments in ancient India ●Elucidate the rich religious sculpture and infer the stories hidden in it. |
To download the full syllabus and check details of map and project work, click on the following link:
CBSE Class 12 History Syllabus 2022-2023: Download in PDF |
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation