CBSE Class 12th Economics Answer Key 2025: The CBSE Class 12 Economics Exam 2025 was held on March 19, 2025. As per the initial student reactions, the paper was moderately difficult. To help the students assess their performance, we provided the CBSE Class 12 Economics Answer Key 2025 in this article. The answer key has been prepared by subject experts and serves as an important resource for students to cross-check their answers and estimate their scores. Using the answer key allows students to learn from their mistakes and improve their preparation for future exams.
CBSE Class 12 Economics Exam Answer Key- Highlights
The CBSE Class 12 Economics question paper had 34 questions for 80 marks. The time allowed to write the paper was 3 hours. All questions were compulsory with some questions having internal choices.
| Feature | Highlights |
| Board Name | Central Board Of Secondary Education (CBSE) |
| Exam Name | CBSE Class 12th Economics Exam |
| Exam Date | March 19, 2025 |
| Duration | 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM (3 hours) |
| Total Marks | 80 |
| Mode | Offline (Pen and Paper) |
| Time Duration | 3 Hours |
| Question Paper Sets: | Multiple Sets (Set 1, Set 2, Set 3, Set 4) |
Features Of CBSE Class 12th Economics Answer Key?
1. Self-Evaluation:
Students can compare their answers with the official solutions to understand their performance.
2. Score Estimation:
By checking the answer key, students can predict their approximate marks before the official results are announced.
3. Identify Mistakes:
Analysing incorrect answers helps students understand their weak areas for improvement in future exams.
Check:
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Paper Analysis - Exam Review & Difficulty Level
- CBSE Class 12 Economics Question Paper 2025 FREE (PDF)
CBSE Class 12 Economics Marking Scheme 2024-2025
Check the CBSE 12th Economics Marking Scheme 2025 in the table below.
| Assessment Type | Marks |
| Theory Exam | 80 |
| Internal Assessment
| (10+10=20) 10 10 |
|
| 100 |
CBSE Class 12 Economics Answer Key 2025
Get here the complete answer key for CBSE Class 12th Economics Exam 2025
1. Identify, which of the following is not to be considered while estimating Revenue Deficit of a country. (Choose the correct option) (1 Mark)
(A) Wages and salaries paid by the government
(B) Interest payments made by the Central Government
(C) Direct Tax Collection
(D) Expenditure incurred on construction of flyover
2. Read the following statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct options given below: (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): In case of public goods no one can be excluded from enjoying the benefits.
Reason (R): Public goods are non-rivalrous and non-excludable in nature.
Options:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
3. Value Addition = _____ - Value of Intermediate Consumption. (Choose the correct option(s) to complete the stated formula.) (1 Mark)
(i) Domestic sales
(ii) Sales – change in stock
(iii) Value of output
(iv) (Number of units produced) × (Price per unit)
Options:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
4. Suppose for an economy, autonomous consumption stands as ₹ 100 crore and total consumption is ₹ 130 crore. The value of induced consumption would be ₹ _____ crore. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
Options:
(A) 30
(B) 80
(C) 100
(D) 130
5. In Keynesian Economics, _____ starts from the origin and is always drawn at an angle of 45°. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
Options:
(A) Consumption curve
(B) Aggregate demand curve
(C) Reference line
(D) Investment curve
6. The monetary policy is formulated by the _____ in the Indian economy. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
Options:
(A) Central Government
(B) State Governments
(C) Reserve Bank of India
(D) World Bank
7. To arrive at the value of equilibrium level of income, there must exist an equality between ex-ante _____ and ex-ante _____. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
(i) Aggregate Demand, Aggregate Supply
(ii) Aggregate Demand, Savings
(iii) Aggregate Demand, Investment
(iv) Savings, Investment
Options:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iv)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
8. The budget under, which the government may spend an amount equal to the revenue it collects is referred as _____ Budget. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
Options:
(A) Surplus
(B) Deficit
(C) Balanced
(D) Deflationary
9. Read the following statements: Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Choose one of the correct options given below: (1 Mark)
Assertion (A): If the value of Marginal Propensity to Save is 0.5, Marginal Propensity to Consume will be equal to Marginal Propensity to Save.
Reason (R): Sum of Marginal Propensity to Consume and Marginal Propensity to Save always equals to unity.
Options:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
10. As the Banker to the Bank, Reserve Bank of India performs all functions except _____. (Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.) (1 Mark)
Options:
(A) Purchase and sale of securities on behalf of the general public
(B) Maintaining current account for Commercial Banks
(C) Clearing and settlement of Interbank transactions
(D) Facilitating governmental transactions
11. (a) "The government generally levies higher Goods and Services Tax (GST) on socially undesirable products like cigarettes, tobacco, liquor etc."
Identify and explain the indicated government budget objective in the above statement. (3 Marks)
Correct Answer:
The government budget objective indicated in the statement is "Regulating Consumption of Harmful Goods" under Fiscal Policy Measures.
- Higher GST on harmful goods such as cigarettes, tobacco, and liquor discourages their consumption.
- It is part of the "Sin Tax" concept, aiming to reduce the negative externalities associated with these products.
- It also helps the government generate additional revenue while promoting public health.
OR
(b) Two friends Ramesh (a software engineer) and Pihu (a bakery owner) are discussing their contribution to the nation's economy through tax payments. Ramesh earns ₹ 8,00,000 per year, which makes him liable to pay income tax. Pihu pays Goods and Service Tax (GST) on the sale of cakes and pastries.
On the basis of the given text, identify whether Ramesh is paying a direct tax or an indirect tax. Explain valid differences between two types of taxes. (3 Marks)
Correct Answer:
- Ramesh is paying a Direct Tax (Income Tax), while Pihu is paying an Indirect Tax (GST).
- Differences Between Direct and Indirect Taxes:
| Basis | Direct Tax | Indirect Tax |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Paid directly by individuals/corporations to the government | Levied on goods and services, collected by businesses and passed to the government |
| Burden of Tax | Cannot be shifted to another person | Can be shifted to the end consumer |
| Examples | Income Tax, Wealth Tax | GST, Excise Duty, Custom Duty |
| Impact | Affects higher-income individuals more | Impacts all consumers equally, regardless of income |
SECTION - B
(Indian Economic Development)
18.(Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.)Options:
(A) Jan-Dhan Yojana
(B) Jan-Aushadhi Yojana
(C) Jan-Soochna Yojana
(D) Jan-Arogya Yojana
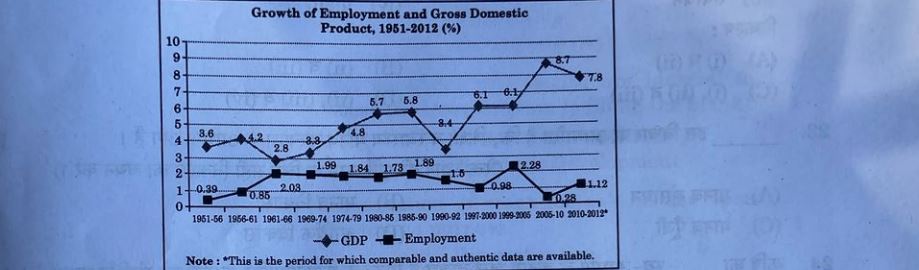
Options:
(A) Informalisation of Workforce
(B) Casualisation of Workforce
(C) Jobless Growth
(D) Formalisation of Workforce
Statement 1: Environmental concerns of waste generation and pollution have become critical, due to reversal of demand and supply relationship.
Statement 2: Environmental crisis happens when the rate of resource extraction is less than that of regeneration of resource.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct option from the following:
Options:(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
(D) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
Options:
(A) Hired Workers
(B) Casual Wage Workers
(C) Regular Salaried Employees
(D) Self-Employed
Options:
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii), (iii), and (iv)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
Correct options include:
- (ii) Processing
- (iii) Assembling
- (iv) Grading
These are key steps in agricultural marketing to improve quality and distribution.
23.(Choose the correct option to fill up the blank.)(1 Mark)Options:(A) Human Resource
(B) Human Development
(C) Human Capital
(D) Economic Development
Options:
(A) Commercialisation
(B) Diversification
(C) Digitisation
(D) Modernisation
Statement 1: In 1978, commune lands were divided into small plots to the individual households for cultivation.
Statement 2: Under the commune system, professionals were sent to work and learn from the countryside.
In the light of the given statements, choose the correct option from the following:
Options:(A) Statement 1 is true and Statement 2 is false.
(B) Statement 1 is false and Statement 2 is true.
(C) Both statements 1 and 2 are true.
(D) Both statements 1 and 2 are false.
Options:
(i) Achieving sustainable development
(ii) Attainment of food security
(iii) Disseminates information regarding emerging technologies
(A) Only (i)
(B) Only (ii)
(C) (i) and (ii)
(D) (i), (ii), and (iii)
Assertion (A): Under the land reforms, the Indian government fixed the minimum land size which could be owned by an individual.
Reason (R): The purpose of land ceiling was to avoid the concentration of land ownership in a few hands.
Options:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
(a) Medhya and Danish both had their own farms.
Medhya invested in a few agricultural courses, learned modern farming techniques, and trained her laborers on best practices related to soil fertility, crop management, and pest control.
Whereas, Danish invested heavily in purchasing advanced farming machinery, irrigation systems, and high-quality seeds.
Do you agree that Danish had made an investment in human capital?
Give a valid reason in support of your answer.
Answer:
No, Danish did not make an investment in human capital. Human capital refers to improvements in skills, education, and health that enhance productivity. Medhya’s investment in training and education aligns with human capital investment, whereas Danish’s focus on machinery and seeds relates to physical capital.
OR
(b) "Expenditure on preventive medicine, curative medicine, and social medicine helps in building human capital and economic development."Do you agree with the given statement? Give valid arguments in support of your answer.
Answer:
Yes, investment in healthcare strengthens human capital. Preventive and curative medicine improves workforce productivity by reducing disease and increasing life expectancy. A healthier population results in a stronger economy due to higher efficiency and lower medical expenses.
Briefly explain the dual pricing policy adopted by China.
Answer:
China’s dual pricing policy allowed industries and farmers to buy inputs at subsidized prices while selling surplus at market rates. This approach encouraged productivity and a gradual shift towards a market economy, balancing state control and economic liberalization.
Download | CBSE Class 12 Economics Answer Key 2025 PDF (Link To Be Active Soon) |
Other Related Links
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation