CBSE Class 10 Science Important Diagrams: Understanding key concepts in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology can be challenging for many Class 10 students. However, mastering the important diagrams for each subject can make a significant difference in your preparation. Diagrams are a crucial part of the CBSE Class 10 Science exam, as they help visualize complex concepts and simplify learning. Instead of just memorizing, practicing these diagrams helps build a deeper understanding of the topics. This article highlights the essential diagrams for Biology, Physics, and Chemistry that are frequently asked in the board exams. By revising these diagrams, students can strengthen their grasp of the subject and improve their chances of scoring high in the CBSE Class 10 Science Exam 2025.
Also, check
Important Diagrams for CBSE Class 10 Science
Mastering diagrams is a crucial part of preparing for the CBSE Class 10 Science exam. These visual representations often carry significant marks and demonstrate a clear understanding of concepts. Below is a list of important diagrams categorized by subject:
Important Diagrams: Physics
Concept | Required Diagram / Focus |
| Human Eye | Structure and working of the eye, specifically the path of light. Diagrams illustrating defects of vision (myopia, hypermetropia) and their correction (using lenses). |
| Electric Circuit | Diagrams showing various components and their symbols. Illustrations of series and parallel connections of resistors and components. |
| Magnetic Field Lines | Diagrams illustrating magnetic field lines around a bar magnet, a current-carrying straight conductor, a circular loop, and a solenoid. |
| Electric Motor | Principle and working of the electric motor with all parts clearly labeled (split ring, armature, magnets, brushes). |
| Electric Generator | Principle and working of the electric generator with labeled parts (slip rings/split rings, armature, brushes). |
| Dispersion of White Light | Diagram showing the dispersion of white light by a prism, clearly labeling the incident ray, refracted rays, and the emergent ray. |
Important Diagrams: Chemistry
Concept | Required Diagram / Focus |
| Electrolytic Refining of Copper | Diagram showing the experimental setup with the impure block of copper (anode) and pure copper strip (cathode), along with the reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. |
| Formation of Ionic Compounds | Electron dot structures (Lewis structures) for compounds formed by ionic bonding, such as NaCl and MgCl₂. |
| Carbon Compounds | Electron dot structures for methane, ethene, ethyne, and simple organic functional groups. |
| Soap Micelle Formation | Diagram illustrating the structure of a soap micelle in water, clearly showing the hydrophobic (non-polar) tail and hydrophilic (polar) head parts of the soap molecule. |
Other Related Links
Important Diagrams: Biology
Concept | Required Diagram / Focus |
| Human Digestive System | All major organs and associated glands. |
| Human Respiratory System | Lungs, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. |
| Human Heart | Internal structure, blood flow, and major blood vessels. |
| Human Excretory System | Kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. |
| Nephron | Structure and function. |
| Structure of a Neuron | Dendrites, cell body, axon, and nerve endings. |
| Reflex Arc | Pathway of nerve impulses. |
| Flower | Longitudinal section showing reproductive parts (sepals, petals, stamens, pistil). |
| Seed Germination | Stages of germination. |
| Plant Root System | Showing root hair and absorption of water. |
| Cross-section of a Leaf | Stomata, guard cells, and mesophyll layers. |
| Binary Fission in Amoeba/Budding in Hydra | Showing stages of asexual reproduction. |
| Reproductive System (Male and Female) | Key organs and their functions. |
| DNA Structure | Double helix model. |
Tips for Diagram Practice:
-
Accuracy: Pay attention to correct labeling, proportions, and neatness.
-
Labeling: Ensure all relevant parts are clearly labeled with accurate scientific terms.
-
Functionality: Understand the function of each labeled part, as questions often ask about the role of specific structures.
-
Practice Regularly: Draw diagrams repeatedly without looking at the book to commit them to memory.
-
Diagram-based Questions: Be prepared to answer questions that require drawing a diagram or interpreting a given diagram.
CBSE Class 10 Science Important Diagrams - Biology
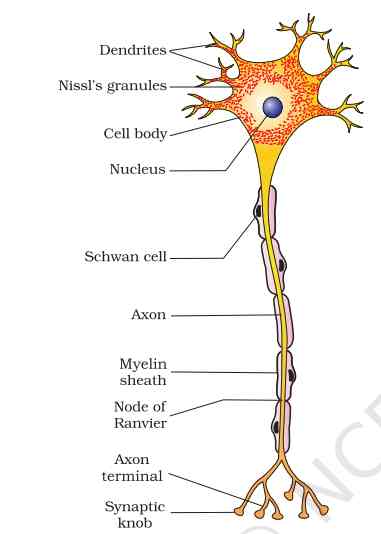
1. Neuron
Neurons or the nerve cells form the basic components of the nervous system. A typical neuron possesses a cell body called as soma, hair like structures called as dendrites and an axon. Dendrites are thin structures that arise from the cell body. These dendrites acquire information from synapses via neurotransmitters and convert them into electrical impulses. These impulses are further carried over to the cell body.
2. Brain
A human brain is composed of three main parts- the forebrain, the midbrain and the hindbrain. These three parts have specific functions.
• Forebrain: This consists of the cerebrum, hypothalamus, and thalamus.
• Midbrain: Consists of the tectum and tegmentum.
• Hindbrain: Is made of the cerebellum, medulla, and pons.

3. Human Digestive system
The primary function of the digestive system is to break down food both mechanically and by the use of enzymes so as to release energy that can be used by the body to perform various functions and proper growth/repair of body cells.
• Food is taken inside mouths where saliva that secreted by salivary glands and contains digestive enzymes like salivary amylase, breaks down starch (contained in food) into sugar.
• Then tongue helps in chewing, moistening, rolling and swallowing it.
• Food moves into the stomach, through the movement of walls of oesophagus.
• Stomach mixes the food hence received with various digestive juices to cause its partial digestion.

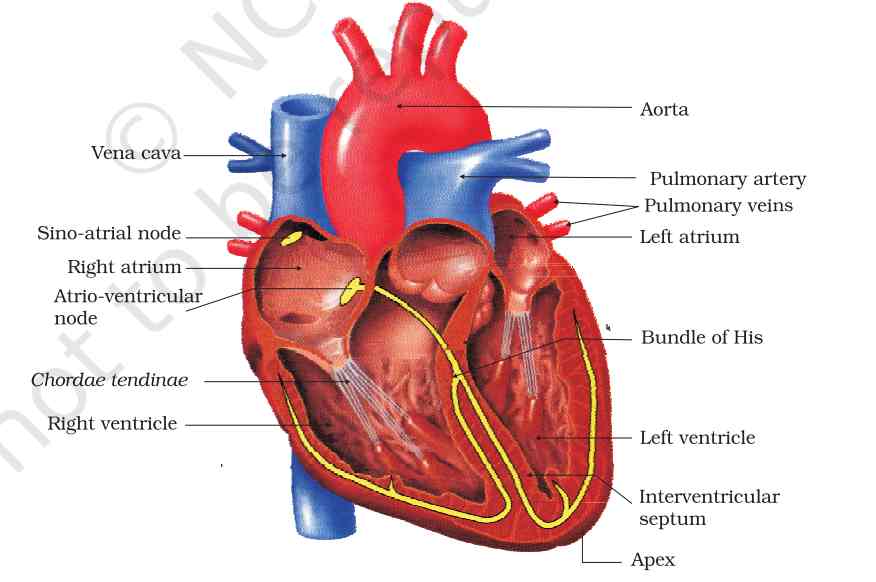
4. Internal Structure of Heart
The human heart has four chambers: two atria (upper) and two ventricles (lower). The right atrium and ventricle make up the right heart, while the left atrium and ventricle form the left heart. The septum, a muscular wall, separates them. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body via the vena cava, then moves to the right ventricle. From there, it is pumped to the lungs via pulmonary arteries for oxygenation. Oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium through pulmonary veins, flows into the left ventricle, and is then pumped to the body through the aorta.
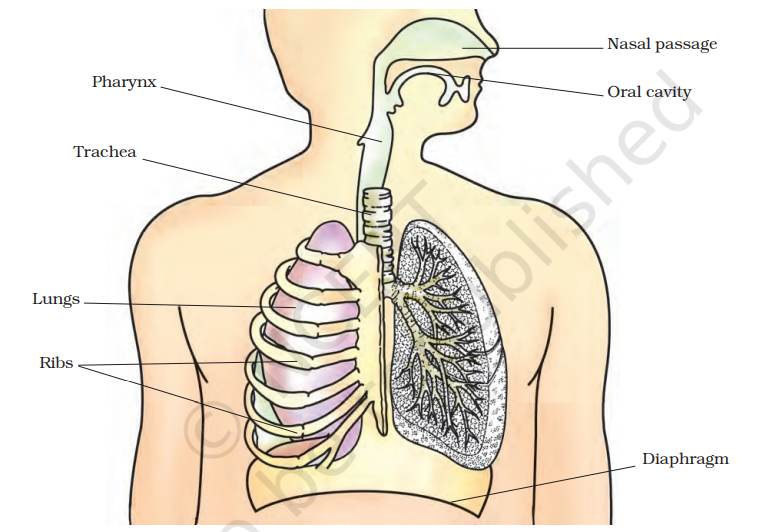
5. Human Respiratory System
It consists of the following parts:
• Nasal cavity: It facilitates the intake of air. It is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air and remove dust and dirt.
• Pharynx: It is a passage behind the nasal chamber and serves as the common passageway for both air and food.
• Larynx: Also known as the sound box as it helps in the generation of sound and thus helps us in communicating.
• Epiglottis: It is a flap-like structure that covers the glottis and prevents the entry of food into the windpipe.
• Trachea: It is a long tube passing through the mid-thoracic cavity.
• Bronchi: The trachea divides into left and right bronchi.
• Bronchioles: Each bronchus is further divided into finer channels known as bronchioles
• Alveoli: The bronchioles end up into the balloon-like structures known as the alveoli
• Lungs: We have a pair of lungs, which are sac-like structures and covered by a double-layered membrane known as pleura.
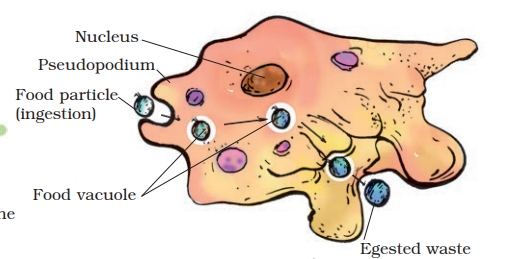
6. Nutrition in Amoeba
Amoeba is a unicellular animal. It takes in food by forming finger like projections called pseudopodia and forms a food vacuole. Inside the food vacuole the food is digested and absorbed. The undigested food is then sent out through the surface of the cell.
IMPORTANT:
- CBSE Class 10 Science Sample Paper For Board Exams 2025 (By CBSE Board)
- CBSE Class 10th Science Exam Pattern 2025
7. Human Female Reproductive System
It consists of the following parts:
• A pair of ovaries: Ovaries produce and store ovum in them. They also produce a female hormone called estrogen.
• Fallopian tubes (Oviducts): They are the site of fertilization. They connect ovaries with the uterus.
• Uterus: Uterus is the site of development for the embryo.
• Cervix: It is located at the lowermost portion of the uterus and is involved in connecting the uterus and the vagina.
• Vagina: It is the part which connects cervix to the external female body parts. It is the route for penis during coitus as well as a foetus during delivery.

8. Budding in Hydra
Budding is a method of reproduction in unicellular organisms like yeast and hydra. In this method a bud like projection is formed on the body of the organism. The bud then develops into a new individual. It then separates from the parent and forms an independent individual.
.jpg)
9. Longitudinal Section (LS) Of A Flower
This flower contains both male and female reproductive parts. The female reproductive part of the flower is known as pistil or carpel. It consists of three subsections stigma, stile and ovary as shown in the following diagram of longitudinal section of flower.
The male reproductive part of the flower is known as stamen. It consists of two subsections anther and filament which are clearly shown in the longitudinal section of flower.
.jpg)
110. Germination of Pollen on Stigma (Fertilisation in flowering plants)
After the pollen grain is transferred to the stigma it produces a pollen tube which passes through the style and enters the ovary and ovule. In the ovule the male germ cell fuses with the female germ cell to produce zygote. This process of formation of single celled zygote is called fertilisation. Zygote then divides several times and forms the embryo which then develops into the seed and the ovary develops into the fruit.

CBSE Class 10 Science Important Diagrams - Physics
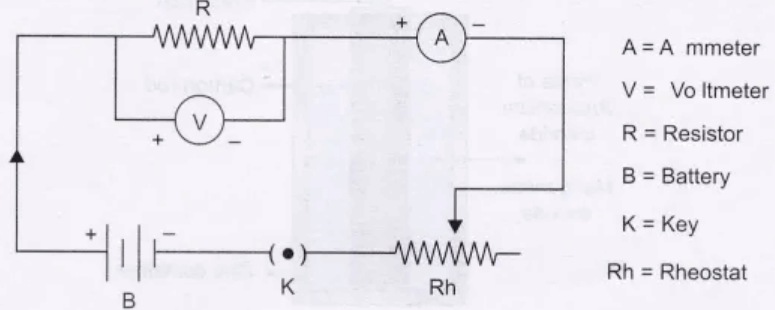
1. Verification of OHM’s Law
Ohm's law states that under constant temperature, the current passing through conductor is directly proportional to potential difference applied across it.
i.e., V = IR
Where,
V = potential difference
R = Resistance (constant)
I = Current
Ohm's law can be verified using the following circuit diagram,
2. AC Generator
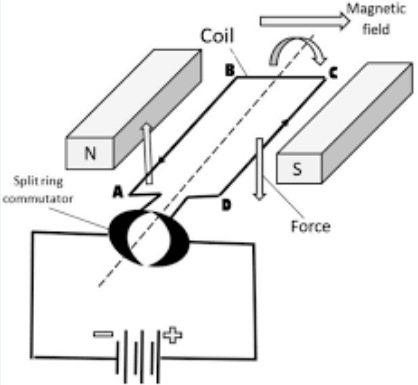
AC generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into alternating form of electrical energy. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When a closed coil is rotated in a uniform magnetic field with its axis perpendicular to the magnetic field, the magnetic field lines passing through the coil change and an induced emf is produced causing the flow of current in it.
3. DC generator
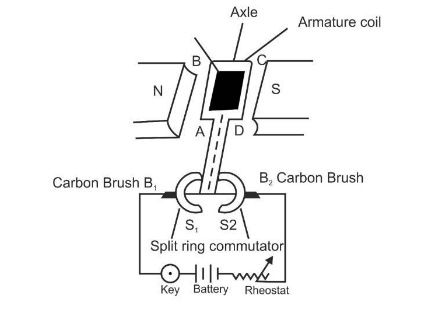
DC generator is a device which converts mechanical energy into the direct form of electrical energy.
DC generator has split ring commutator instead of slip rings in the AC generator. Split ring commutator consists of two semicylindrical brass rings S1 and S2 rigidly attached to the two ends of the armature coil. As the armature coil rotates, the two split rings also rotate about the same axis of rotation.
4. Human eye
.jpg)
5. Refraction of Light through a Glass Prism
Prism is a transparent optical object with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. At least two of the flat surfaces must have an angle between them.
When a ray of light enters the glass prism it gets deviated two times. First when it enters the glass prism and second when it comes out of the prism. The emergent ray is divided by an angle to the incident ray. This angle is called the angle of deviation.

6. Recombination of the Spectrum of White Light
When a beam of white light is passed through a glass prism, it is split up into its component colours. When these colours are allowed to fall on an inverted glass prism it recombines to produce white light.
.jpg)
7. Rainbow Formation
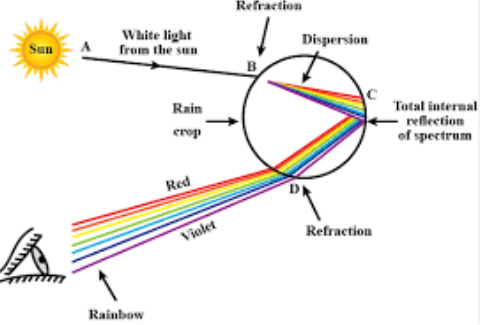
A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain shower. It is caused by the dispersion of sunlight by water droplets present in the atmosphere. The water droplets act like small prisms. They refract and disperse the sunlight which again reflected internally and finally refracted again when coming out of the rain drops. Due to the dispersion and internal reflection of sunlight by the water droplets, we see the rainbow.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation