CBSE Board Class 12 Chemistry MCQs (With Answers) 2024: The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) 12th Class Chemistry examination is planned to be conducted on February 27, 2024, Tuesday. This paper holds significant importance for science students. With the diverse range of topics and concepts covered in the syllabus, mastering this subject is challenging. To help students in their preparation for the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam 2024, Jagran Josh presents a comprehensive set of over 30 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) along with their answers, expertly curated to cover various chapters and topics of the syllabus.
These MCQs are from previous year's papers and other online resources to assess students' understanding of fundamental principles, theories, and applications in Chemistry. These MCQs offer a valuable tool for students aspiring to secure good marks in their CBSE 12th-grade Chemistry examination 2024. Scroll down, download, and test your knowledge.
MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2024
Below is the list of 30+ MCQs from Class 12 Chemistry. The answers are highlighted for your reference.
1. Choose the compound which is more acidic than phenol :
(a) o-nitrophenol
(b) ethanol
(c) o-methylphenol
(d) o-methoxyphenol
2. The most common oxidation state for all lanthanoids is :
(a) + 5
(b) + 2
(c) + 3
(d) + 4
3. A reaction follows second order kinetics. How is the rate of reaction affected if the concentration of the reactant is reduced to half ? Choose the correct value from the following :
(a) four times
(b) eight times
(c) 1/4 of the original value
(d) three times
4. Solutions of two electrolytes X and Y are diluted. Molar conductivity of X increases 25 times whereas that of Y increases 1·5 times. Which one is a stronger electrolyte ?
(a) X
(b) Y
(c) Both X and Y
(d) None of the above
5. Unit of rate constant for the zero order reaction is :
(a) s-1
(b) mol-1Ls-1
(c) mol-2L2s-1
(d) mol L⁻¹ s⁻¹
6. Which type of isomerism is shown by the complexes [Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl3 ?
(a) Linkage
(b) Ionisation
(c) Optical
(d) Solvate
7. Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one can be distinguished by :
(a) Fehlings's test
(b) Sodium bicarbonate test
(c) Tollen's test
(d) Iodoform test
8. Oxidation state of central metal atom in the given complex is : [Co(NH3)4(H2O)2]Cl3
(a) + 2
(b) + 3
(c) + 1
(d) + 4
9. A galvanic cell can behave as an electrolytic cell when :
(a) Ecell = Eext
(b) Ecell > Eext
(c) Ecell = 0
(d) Eext > Ecell
10. The rate law for a particular reaction is given as rate = k[A][B]2 How is the rate of reaction affected if we double the concentration of B ? Choose the correct option :
(a) two times
(b) four times
(c) three times
(d) becomes half (1/2)
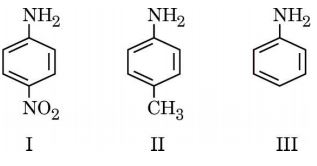
11. Three compounds are given below :
The correct decreasing order of their basic strength is :
(a) II > III > I
(b) III > II > I
(c) III > I > II
(d) I > III > II
12. The helix structure of protein is stablized by:
(a) peptide bond
(b) hydrogen bond
(c) disulphide bond
(d) van der Walls forces
13. Nucleic acids are polymers of:
(a) nucleosides
(b) D-ribose
(c) amino acids
(d) nucleotides
14. Which of the following is a strong oxidising agent? (At. no. Mn= 25, Zn=30, Cr=24, Sc=21)
(a) Mn3+
(b) Zn2+
(c) Cr3+
(d) Sc3+
15. A compound formed by elements P and Q crystallizes in a cubic structure where P atoms are at the corners of a cube and Q atoms are at the face centres. The formula of the compound is:
(A) P2Q
(B) PQ3
(C) PQ
(D) PQ
16. Nitrogen is unable to form pentahalides because of:
(A) the presence of s and p orbitals.
(B) the absence of both p and d orbitals.
(C) the absence of d orbitals.
(D) all of the above
17. Which of the following hydrogen halides is most volatile?
(A) H-F
(B) H-I
(C) H-Br
(D) H-Cl
18. The oxidation number of Co in [Co(en) gl2(SO4)3 is:
(A) +2
(B) +3
(C) +4
(D) +6
19. Which of the following ligands form a 'chelate' complex with metal ion?
(A) H₂O
(B) CN
(C) C2O2-4
(D) Cl-
20. The coordination number of Cr in [CrCl2(ox)2]³- is:
(A) 6
(B) 5
(C) 4
(D) 3
21. Cubic close packing of equal sized spheres is described by:
(A) ACB ACB ACB
(B) AB AB AB ...
(C) ABC ABC ABC...
(D) AB AC AC AB...
22. Which stoichiometric defect does not change the density of the crystal?
(A) Frenkel defect
(B) Schottky defect
(C) Interstitial defect
(D) F-centres
23. An antifreeze solution is prepared from 222.6 g of ethylene glycol C2H4(OH)2 and 200 g of water. Calculate the molality of the solution. If the density of this solution be 1.072 gmL-1, what will be the molarity of the solution?
(a) 7.20 M
(b) 12.03 M
(c) 9.11 M
(d) 6 M
24. The osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to
(a) the molecular concentration of the solute
(b) the absolute temperature at a given concentration
(c) the lowering of vapour pressure
(d) all the above.
25. The average osmotic pressure of human bloood is 7.8 bar at 37°C. What is the concentration of an aqueous solution of NaCl that could be used in blood stream?
(a) 0.15 mol L-1
(b) 0.30 mol L-1
(c) 0.60 mol L-1
(d) 0.45 mol L-1
26. Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by
(a) SN1 mechanism
(b) SN2 mechanism
(c) SN1 and SN2 mechanism
(d) neither SN1 nor SN2 mechanism
27. Dehydration of alcohol to ethers is catalysed by
(a) conc. H2SO4 at 413 K
(b) Hot NaOH
(c) Hot HBr
(d) Hot HNO3
28. Which of the following alcohols gives 2-butenc on dehydration by conc. H2SO4?
(a) 2-methyl propene-2-ol
(b) 2-methyl 1 -propanol
(c) Butane-2-ol
(d) Butane 1-ol
29. Order of esterification of alcohols are
(a) 3° > 1° > 2°
(b) 2°> 3° > 1°
(c) 1 ° > 2° > 3°
(d) None of these
30. The functional group which is found in amino acid is-
(a)-COOH
(b) -NH2
(c) -CH3
(d) both (a) and (b)
31. Which base is present in RNA but not in DNA?
(a) Uracil
(b) Cytosine
(c) Guanine
(d) Thymine
32. Which of the following factors is not responsible for the denaturation of proteins?
(a) Heat
(b) Charge
(c) PH change
(d) Organic solvents
33. Mn3+ is not stable in acidic medium, while Fe3+is stable because
(a) O2 oxidises Mn2+ to Mn3+
(b) O2 oxidises both Mn2+ to Mn3+ and Fe2+ to Fe3+
(c) Fe3- oxidises H2O to O2
(d) Mn3+ oxidises H2O to O2
34. The first order reaction takes 80 minutes to complete 99.9%. What will be its half-life?
(a) 8 min
(b) 16 min
(c) 24 min
(d) 32 min
35. In the first order reaction, the concentration of the reactant is reduced to 1/4th in 60 minutes. What will be its half-life?
(a) 120 min
(b) 40 min
(c) 30 min
(d) 25 min
We hope these MCQs helped you improve your knowledge. For more information and updates keep checking jagranjosh.com
Related:
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Deleted syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry sample papers 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24 PDF (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Deleted Syllabus (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Papers with Solution PDF Download
- CBSE Class 12 Additional Practice Questions
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper 2023-24 with Solution and Additional Practice Questions
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation