NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6: Physics is considered to be one of the toughest subjects. It is not unusual for students to get afraid of it. Consistent practice is key to mastering physics. Students must regularly practice numerical questions for better understanding and clarity. The exercises given in NCERT textbooks are crucial for preparing students for the 2025 examination as there is a chance that the Board exam may carry questions from textbooks.
To help students, we have provided NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction solutions in this article. These solutions have been prepared by the subject matter experts.
Also Check:
| CBSE Class 12 Physics Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme for 2025 |
Download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction from the direct link given in this article.
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction Solutions
Given below are the questions and solutions from NCERT Class 12 Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction.
EXERCISES
Q. Predict the direction of induced current in the situations described by the following figures.
(a) 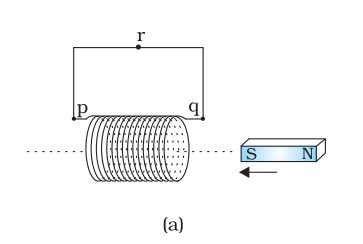
(b) 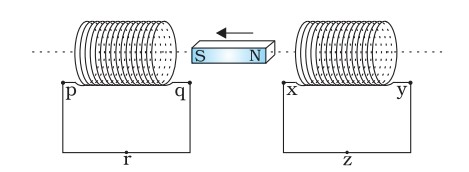
(c) 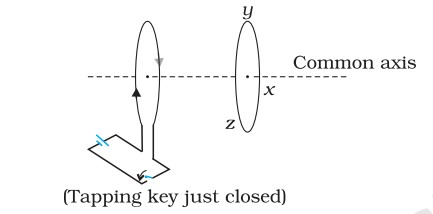
(d) 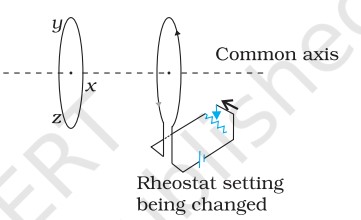
(e) 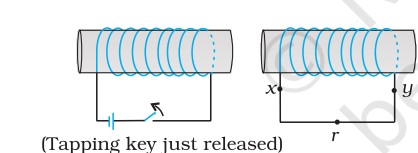
(f) 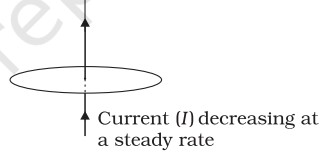
Sol. (a) Direction: qrpq
(b) Direction: prqp; yzxy
(c)Direction: yzxy
(d) Direction: zyxz.
(e) Direction: xryx
(f) Direction: No induced current
Q. Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situations described by figure (a) A wire of irregular shape turning into a circular shape; (b) A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.
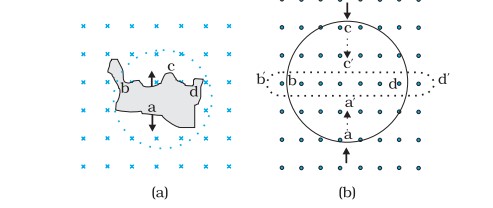
Sol. According to Lenz’s law (given by German physicist Heinrich Friedrich Lenz), the polarity of induced emf is such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it. Lenz’s law opposes the very cause that causes it.
(a) Since the passing flux is increasing, the direction of induced current as per Lenz’s law will be: adcb
(b) Since the passing flux is decreasing, the direction of induced current as per Lenz’s law is: adcba.
Q. A long solenoid with 15 turns per cm has a small loop of area 2.0 cm² placed inside the solenoid normal to its axis. If the current carried by the solenoid changes steadily from 2.0 A to 4.0 A in 0.1 s, what is the induced emf in the loop while the current is changing?
Sol. Given,
n = 15 turns / cm
a = 2 sq. cm
dt = 0.1 s
Ii = 2 A
If = 4 A
θ= 0
Φ=B.A. cosθ…………………………(1)
Initial magnetic field, Bi =μ0nIi
Substituting,
Bi = (4π x 10-7).(1500).(2)
Or Bi = 3.77x10-³ T
Final magnetic field, Bf = (4π x 10-7).(1500).(4)
= 7.54x10-³T
Initial value of flux = Bi.A.cos0
= (3.77x10-³).(2x10-⁴)
= 7.54x10-⁷Wb
Final value of flux = Bf.A.cos0
= (7.54x10-³). (2x10-⁴)
= 1.51x10-⁶ Wb
Therefore induced emf
E = Difference in flux / Corresponding time interval
Or E = [(1.51x10-⁶ Wb)–(7.54x10-⁷ Wb)] / 0.1
Or E = 7.56x10-⁶ V
Q. A rectangular wire loop of sides 8 cm and 2 cm with a small cut is moving out of a region of uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.3 T directed normal to the loop. What is the emf developed across the cut if the velocity of the loop is 1 cm s-¹ in a direction normal to the (a) longer side, (b) shorter side of the loop? For how long does the induced voltage last in each case?
Sol. Given,
length = 8 cm
breadth = 2 cm
B = 0.3 T
velocity = 1 cm / s
Area of the loop
A = 0.0016 sq. m
The loop is moving with the given velocity. As long as the loop lies completely in the magnetic field, no emf will be induced as there is no change in the flux. But the moment it starts slipping into outer space, the flux passing through the loop decreases and an emf is induced. Since the circuit is not complete, current will not flow.
Value of initial flux = BAcos0
= 0.3 x 0.0016
= 0.00048 Wb
Value of final flux = 0,
(a) In this case the time elapsed is
t = distance / speed
= 2 / 1
= 2 s
So induced emf
E = dФ/ dt
E = (0.00048–0) / 2
Or E = 2.4x10-⁴V
The voltage will last 2 seconds.
(b) Here the time elapsed is
t = 8 / 1
= 8 s
Thus induced emf
E = dФ/ dt
E = 0.00048 / 8
Or E = 6x10-⁵V
The voltage will last 8 seconds.
Q. A 1.0 m long metallic rod is rotated with an angular frequency of 400 rad s-¹ about an axis normal to the rod passing through its one end. The other end of the rod is in contact with a circular metallic ring. A constant and uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T parallel to the axis exists everywhere. Calculate the emf developed between the centre and the ring.
Sol. Given,
r = 1 m
w = 400 rad / s
B = 0.5 T
Ф =B.A. cos 0
= 0.5 x 3.14 x 1 x 1
= 1.571 Wb
Ф =B.A.cos 180
= -1.571 Wb
w = 400
Or f = 400 / 2 x 3.14 = 63.66 / s
Therefore
E = [ 1.571–(- 1.571)] / 0.0314
Or E = 100 V
Q. A horizontal straight wire 10 m long extending from east to west is falling with a speed of 5.0 m s-¹, at right angles to the horizontal component of the earth’s magnetic field, 0.30 x 10-⁴ Wb m-² . (a) What is the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the wire? (b) What is the direction of the emf? (c) Which end of the wire is at the higher electrical potential?
Sol. Given,
l = 10 m
v = 5 m / s
H = 0.3x10-⁴ Wb m²
(a) Einst = Blv
= (0.00003).(10).(5)
= 1.5x10-³ V
(b) West to east
(c)eastern end.
Q. Current in a circuit falls from 5.0 A to 0.0 A in 0.1 s. If an average emf of 200 V induced, give an estimate of the self-inductance of the circuit.
Sol. Given,
dI = 5–0 = 5 A
dt = 0.1 s
Eavg = 200 V
E = L.dI/dt
Substitution gives
L = 4 H
Q. A pair of adjacent coils has a mutual inductance of 1.5 H. If the current in one coil changes from 0 to 20 A in 0.5 s, what is the change of flux linkage with the other coil?
Sol. Given,
M = 1.5 H
dI = 20 A
dt = 0.5 s
d(NФ) / dt = d(MI) / dt
Substituting values,
d(NФ) = 30 webers
To download these solutions in pdf, refer to the below link:
| Download NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Induction Solutions PDF |
Also, check
- CBSE 12th Date Sheet 2025 Download PDF
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Study Material for 2025
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Most Repeated Questions
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Competency-Based Questions With Answer Key 2024-25
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Topper Answer Sheet for 2025 Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics 90 Days Study Plan for 2025 Exam
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 (2024-2025) All Subjects
- NCERT Books for CBSE Class 12 - Latest Edition
- NCERT Rationalised Content for Class 12
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation