Microbes in Human Welfare CBSE Notes: Revision notes are short notes that highlight important information discussed in the chapter. Such notes should not be lengthy but to the point. People may use flow charts and illustrations in revision notes. These notes serve the purpose of quick revision a day or two before the exams.
In this article, you will find revision notes on Microbes in Human Welfare, Chapter 8 of CBSE Class 12 Biology. This chapter involves the names of microbes and their roles, which sometimes become difficult to remember. The notes provided here are crisp and include all the important names. These revision notes are taken from the revised NCERT Class 12 Biology textbook. Check out and download the CBSE Class 12 Chapter 8 Microbes in Human Welfare notes below.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 8 Microbes in Human Welfare Revision Notes
Important Terms
| 1 BOD- Biochemical Oxygen Demand 2 GAP- Ganga Action Plan 3 YAP- Yamuna Action Plan 4 KVIC- Khadi and Village Industries Commission 5 LAB- Lactic Acid Bacteria 6 Baculovirus- Pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods 7 Effluent- The product of primary treatment of sewage. 8 Fermentors- A very large vessel where microbes are grown on an industrial scale. 9 Flocs- mass of mesh like structure formed by Bacteria and fungi. 10 Prions- The proteinaceous infectious agent. 11 Methanogens - Bacteria producing methane. 12 STPs- Sewage Treatment Plants 13 IARI- Indian Agricultural Research Institute 14 IPM- Integrated Pest Management |
Microbes in Household
- LAB (Lacto bacillus) grows in milk and converts it into curd. It produces lactic acid.
- BAKER'S YEAST (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) -It causes fermentation &produces carbon dioxide.
- TODDY-Traditional drink prepared by fermenting palm sap.
- Cheese- Swiss cheese (large amounts of CO2 are produced by Propionibacterium sharmanii)
- Roquefort cheese— by fungi.
Fermented Beverages
- Yeast ferments malted cereal and fruit juice to produce ethanol.
- With distillation—whisky, brandy, rum
- Without distillation—wine, beer
Chemicals
Acids:
- Aspergillus niger- citric acid
- Acetobacter aceti- acetic acid
- Clostridium butylicum- butyric acid
- Lactobacillus– lactic acid
Lipases
- Used in detergent formulation to remove oil stain of laundry.
Streptokinase
- Produced by Streptococcus. used as a clot buster for removing clots from blood vessels
Cyclosporin-A
- Used as an immunosuppr essive agent in organ transplant.
- produced by Trichoderma polysporum.
Statins
- Produced by Monascus purpureas
- It lowers blood cholesterol
Antibiotics
- Penicillin -It is produced by Penicillium notatum
Microbes to control pests and diseases
- Bacillus thuringiensis - produces protein which kills the caterpillars.
- Trichoderma - fungi kills root borne pathogens.
- Baculovirus–(genus. Nucleopolyhedrovirus-) attacks specific insects and other arthropods.
- Biological control-lady bird beetle to get rid of aphids and dragon flies to eradicate mosquitoes.
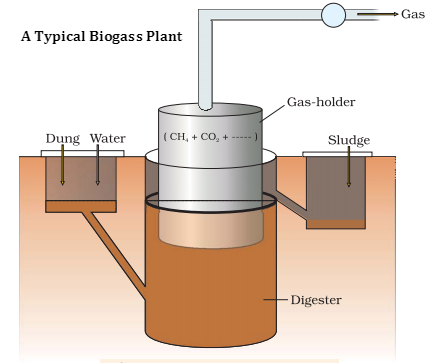
Microbes in the Production of Bio-Gas
- Methanogens (e.g.) Methanobacterium.
- Act on cellular material to produce methane, seen in anaerobic sludge digesters, rumen of cattle, flooded rice fields and in cattle dung.
Microbes as biofertilizers
- Bacteria: Symbiotic Bacteria (Rhizobium) and free living Bacteria (azospirillum and azatobacter) fix atmospheric nitrogen and enrich soil nutrients.
- Cyanobacteria: Anabaena, Nostoc, and Oscillatoria enrich the organic matter of soil through photosynthesis.
- Fungi (e.g.) Glomus fungi associate with the roots of higher plants to absorb phosphorous and give it to plants. It gives resistance to root-borne pathogens.
Microbes used in sewage treatment
- Primary Treatment: 1. Filtration 2. Sedimentation
- Secondary Treatment: 1. Aerobic Digestion 2. Anaerobic digestion
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation