The JEE Main Physics Question Paper will test candidates on their grasp of fundamental physics concepts across subjects like Mechanics, Thermodynamics, Waves, Optics, and more. Every year, the eczema patterns remain constant, providing students with a fair chance to showcase their knowledge and problem solving skills. In the examination candidates will come across MCQ and numerical questions , with an emphasis on accuracy and time management.
JEE Main 2024 Physics Question Paper
The 2024 JEE Main exam was conducted in two sessions for paper 1 and paper 2. The exams were conducted in two shifts (morning and evening). Check and download all the questions and answers from last year's JEE Main exam by clicking the links below:
JEE Main 2024 Session 1 Question Paper
JEE Main 2024 Session 2 Question Paper
JEE Main 2023 Physics Question Paper
This below information offеrs downloadablе PDF links to thе JEE Main 2023 quеstion papеrs from diffеrеnt shifts and еxam datеs, availablе in both English and Hindi languagеs. Click on the link below to access the question paper:
JEE Main Physics Important Questions Asked
Given below is a list of JEE Main Physics questions aksed over the time in the last few years.
1. Two cars are approaching each other at an equal speed of 7.2 km/hr. When they see each other, both blow horns having frequency of 676 Hz. The beat frequency heard by each driver will be _ Hz. Velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s.]
2. A uniform and homogeneous rod has resistance R. If the rod is cut into 5 equal parts and connected in parallel find equivalent resistance ?
3. Acceleration due to earth on the surface is g0. If mass of earth remains same but radius is half, then find the acceleration on the surface for new system :
(1) g0/2 (2) g0 (3) 2 g0 (4) 4 g0
4. Two particles having mass 4g & 25g have the same kinetic energy. Find the ratio of their momentum?
(1) 2/5 (2) 2 /3 (3) 4/5 (4) 3/4
5. An object of mass 1000 kg is moving with 6 m/s. Find speed of object is mass 200 kg is added to it ?
(1) 4 m/s (2) 5 m/s (3) 8 m/s (4) 6 m/s
6. If the electron revolving in the third Bohr's orbit of hydrogen species has radius R, then what will be its radius in fourth orbit in terms of R.
(1) 25R/9
(2) 16R/9
(3) 36R/9
(4) 9R/16
7. A banked road of radius 400 m is there with base separation between the rails is 1.5 m, if speed of a car for safe turning is 12 m/s, then find height of one rail w.r.t to second rail?
(1) h = 0.054 m
(2) h = 0.1 m
(3) h = 0.001 m
(4) h = 0.2 m
8. Statement-1 : Angular momentum and Plank constant have same dimensions. Statement-2 : Moment of force and linear momentum have same dimensions.
(1) Both statements are true
(2) Both statements are false
(3) Statement 1 is true and 2nd is false
(4) Statement 2 is true and 1st is false
9. S1 Viscosity coefficient of gas is less than liquid S2 Surface tension decreases if insoluble impurities are added.
(1) S1 is true, S2 is true
(2) S1 is false, S2 is false
(3) S1 is true, S2 is false
(4) S1 is false, S2 is true
10. Galvanometer shows deflection of π/3 where I1 = 200 µA current is passed what will be the current when the deflection in galvanometer is π/10
(a) 600 µA
(b) 60 µA
(c) 20 µA
(d) 40 µA
11. A point charge q is placed at a centre of a charged ring of total charge Q. Find tension in the ring.
Also Check:
List of Top 10 JEE Coaching Institutеs in India
12. Light in incident on a convex lens of focal length 40 cm. And a metal plate is placed on focus of lens & photo current is measure to be I. Find new photocurrent if lens is replaced by another lens focal length of 20 cm & metal plate is kept on its focus?
13. A circular hole of radius (a/2) is cut out of a circular disc of radius 'a' shown in figure. The centroid of the remaining circular portion with respect to point 'O' will be:
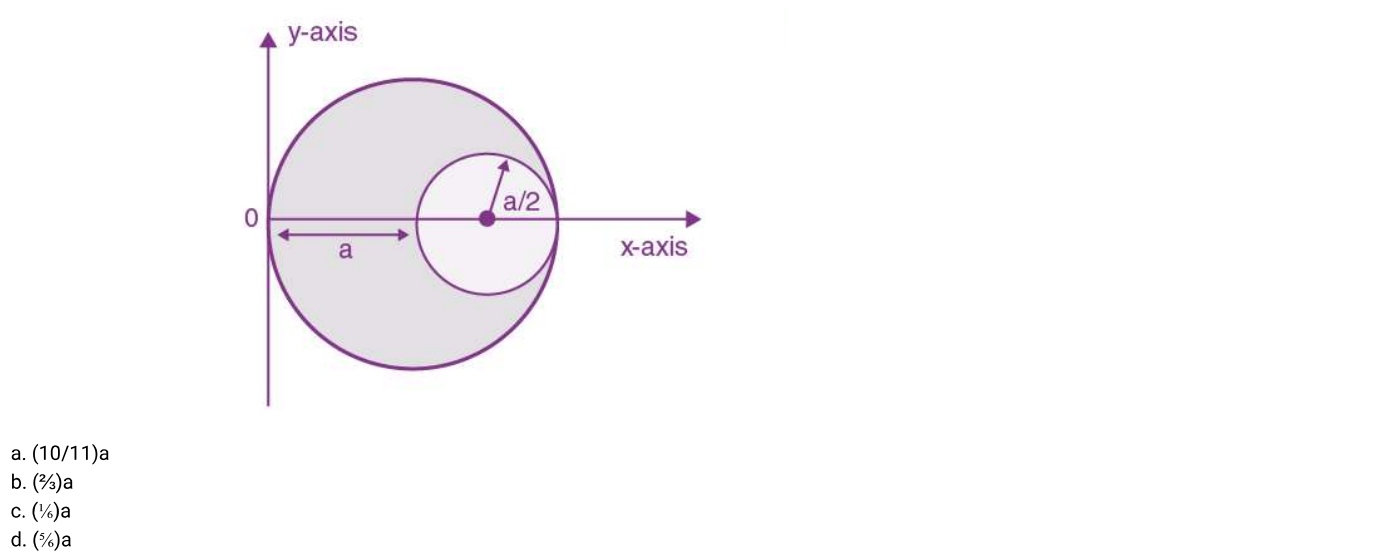
14. If one mole of an ideal gas at (Pi, V4) is allowed to expand reversibly and isothermally (A to B) its pressure is reduced to one-half of the original pressure (see figure). This is followed by a constant volume cooling till its pressure is reduced to one-fourth of the initial value (B→C). Then it is restored to its initial state by a reversible adiabatic compression (C to A). The net work done by the gas is equal to:

15. In the given figure, a body of mass M is held between two massless springs, on a smooth inclined plane. The free ends of the springs are attached to firm supports. If each spring has spring constant k, the frequency of oscillation of given body is:

Related -
- JEE Main Marking Scheme and Paper Pattern
- JEE Main Mathematics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Complete Syllabus
- Revised and Updated JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus, Download PDF Here
- JEE Advanced Exam Pattern and Marking Scheme: Download PDF
- NEET Physics Syllabus: Download Detailed Syllabus in PDF Here
- JEE Main Syllabus, JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Exam Pattern, JEE Main paper pattern
- JEE Main Eligibility
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation