CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2023: The Central Board of Secondary Examination (CBSE) Class 12 examinations have begun, and the highly important science stream exam of Chemistry was conducted today, February 28, 2023, from 10:30 AM to 1:30 PM. Millions of students gave the exam, and all had varied experiences. Some found it tough, others too simple. One long-running after-exam tradition among students is discussing the question papers. It’s not a recommended practice, but quite irresistible. However, going over answers after exams can also reveal mistakes in questions. Students can know how and what to dispute in case their score suffers due to an external mistake. But it's important to know the SET 1, 2, 3 and 4 CBSE Class 12 answer key for that. The board doesn’t release the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam 2023 answer key this soon. However, you can check the but correct answer key for the CBSE class 12 Chemistry paper 2023 here. It’ll help you get a faint idea of your exam score. You can refer to the CBSE class 12 Chemistry paper 2023 answer key in this article.
Related:
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper Answer Key 2023
CBSE hasn’t released the 2023 class 12 Chemistry question paper or answer key yet. However, you can check out the genuine question paper and CBSE Class 12 Chemistry answer key 2023 here. The official consensus of the paper was moderately difficult.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2023 Answer Key
Section- A
- Which one of the following has lowest pKa value?
(a) CH3-COOH
(b) O2N-CH2-COOH
(c) Cl-CH2-COOH
(d) HCOOH
Answer: (b) O2N-CH2-COOH
- Which of the following cell was used in Apollo space programme?
(a) Mercury Cell
(b) Daniel Cell
(c) H2-O2 Fuel cell
(d) Dry Cell
Answer: (c) H2-O2 Fuel cell
- Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Fe3+ (aq) + e- —> Fe2+ (aq) Eo = + 0.77 V
MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ + 5e- —-> Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l) Eo = + 1.51V
What is the cell potential for the redox reaction?
(a) -2.28 V
(b) - 0.74 V
(c) + 0.74 V
(d) + 2.28 V
Answer: (c) +0.74 V
- The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25o C:
A(g) + B(g) —-> C(g) + D(g)
| Initial [ A(g) ] / mol / dm-3 | Initial [B(g)] / mol / dm-3 | Initial rate / mol / dm-3 |
| 3.0 x 10-2 | 2.0 x 10-2 | 1.89 x 10-4 |
| 3.0 x 10-2 | 4.0 x 10-2 | 1.89 x 10-4 |
| 3.0 x 10-2 | 4.0 x 10-2 | 7.56 x 10-4 |
What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
|
| Order with respect to A(g) | Order with respect to B(g) |
| (a) | Zero | Second |
| (b) | First | Zero |
| (c) | Second | Zero |
| (d) | Second | First |
Answer: To be updated
- The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2-
(a) 1.82 BM
(b) 2.82 BM
(c) 4.42 BM
(d) 5.46 BM
(Atomic no : Ni= 28)
Answer: (a) 1.82 BM
- Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6 ?
(a) Ni3+
(b) Co3+
(c) Mn2+
(d) Mn3+
Answer: (b) CO3+
- Which of the following aqueous solution will have highest boiling point?
(a) 1.0 M KCl
(b) 1.0 M K2SO4
(c) 2.0 M KCl
(d) 2.0 M K2SO4
Answer: to be updated
- A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half equations below:
Sn2+(aq) + 2e- -->Sn(s)Eo=-0.14 V
Fe3+(aq)+e- --> Fe2+ (aq)Eo=+0.77 V
Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
(a) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is -0.91 V.
(b) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
(c) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V.
(d) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.63 V.
Answer: to be updated
- Amides can be converted into amines by the reaction named
(a) Hoffmann degradation
(b) Ammonolysis
(c) Carbylamine
(d) Diazotisation
Answer: (a) Hoffmann degradation
- Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose.
(b) On heating with HI it forms n-hexane.
(c) It is present in pyranose form.
(d) It gives 2,4 DNP test.
Answer: (d) It gives 2,4 DNP test.
- Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation?
(a) Butanol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
(d) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
Answer: (d) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
12. Four half reactions I to IV are shown below:
- 2Cl- —> Cl2 + 2e-
- 4OH- —-> O2 + 2H2O + 2e-
- Na+ + e- —-> Na
- 2H+ + 2e- —-> H2
Which two of these reactions are most likely to occur when concentrated brine is electrolysed?
(a) I and III
(b) I and IV
(c) II and III
(d) II and IV
Answer:
13. Which property of transition metals enables them to behave as catalysts?
(a) High melting point
(b) High ionisation enthalpy
(c) Alloy Formation
(d) Variable oxidation states
Answer: (d) Variable oxidation states
14. Which of the following would not be a good choice for reducing nitrobenzene to aniline?
(a) LiAlH4
(b) H2/Ni
(c) Fe and HCl
(d) Sn and HCl
Answer: (a) LiAlH4
For the questions 15 to 18 , two statements are given - one labeled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R ). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c ), and (d) as given below:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- Assertion (A) : Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body.
Reason (R) : Vitamin C is fat soluble and is excreted from the body in urine.
Answer: (c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false
- Assertion (A) : The half life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of the reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concentration.
Reason (R) : In first order kinetics when concentration of reactant is doubled, its half life is doubled.
- Assertion (A) : Bromination of benzoic acid gives m-bromobenzoic acid.
Reason (R) : Carboxyl group increases the electron density at the meta position.
Answer: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- Assertion (A): EDTA is a hexadentate ligand.
Reason (R) : EDTA has 2 nitrogen and 4 oxygen donor atoms.
Answer: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- (a) Which of the following species cannot act as a ligand? Give reason.
OH-, NH+4, CH3NH2, H20
Answer: NH4+ ion cannot act as a ligand as it does not possess any lone pair of electrons which it can donate to central metal ion. Therefore, it does not form complexes.
(b) The complex [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 is red in colour. Give IUPAC name of its linkage isomer.
Answer: The complex [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl2 is obtained in red colour when the nitrite ligand is bound through oxygen.
IUPAC name of its linkage isomer is - Pentamminenitrocobalt(III) chloride.
- For the pair phenol and cyclohexanol, answer the following:
(a) Why is phenol more acidic than cyclohexanol?
(b) Give one chemical test to distinguish between the two.
Answer:
(a) Phenol is more acidic than cyclohexanol because the phenoxide ion is more stable than the alkoxide ion. Phenoxide ion is stabilised by resonance whereas no resonance structures are possible for alkoxide ion of cyclohexanol.
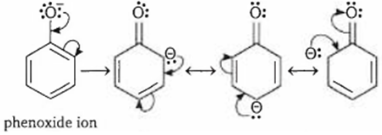
(b) Bromine water test can be used to distinguish between phenol and cyclohexanol. Phenol decolorises bromine water and gives white ppt. of 2, 4, 6- tribromophenol. But cyclohexanol does not give this test.
- (a) (i) Draw the zwitter ion structure for sulphanilic acid.
(ii) How can the activating effect of -NH2 group in aniline be controlled?
Answer:
(a) (i) Zwitter ion structure for sulphanilic acid:
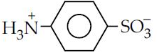
(ii) The activating effect of −NH2 group can be controlled by acetylation of −NH2 group.
Also Read: CBSE Chemistry Class 12 Syllabus 2022-2023
Also Read: CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Notes
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Paper 2022-23
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Deleted Syllabus 2022-23
Also Read: CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Practice Paper 2023
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation